Genetic network identifies novel pathways contributing to atherosclerosis susceptibility in the innominate artery
- PMID: 25115202
- PMCID: PMC4142055
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-7-51
Genetic network identifies novel pathways contributing to atherosclerosis susceptibility in the innominate artery
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis, the underlying cause of cardiovascular disease, results from both genetic and environmental factors.
Methods: In the current study we take a systems-based approach using weighted gene co-expression analysis to identify a candidate pathway of genes related to atherosclerosis. Bioinformatic analyses are performed to identify candidate genes and interactions and several novel genes are characterized using in-vitro studies.
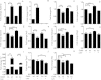
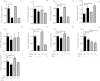
Results: We identify 1 coexpression module associated with innominate artery atherosclerosis that is also enriched for inflammatory and macrophage gene signatures. Using a series of bioinformatics analysis, we further prioritize the genes in this pathway and identify Cd44 as a critical mediator of the atherosclerosis. We validate our predictions generated by the network analysis using Cd44 knockout mice.
Conclusion: These results indicate that alterations in Cd44 expression mediate inflammation through a complex transcriptional network involving a number of previously uncharacterized genes.
Figures
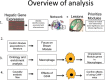
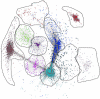
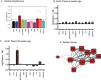
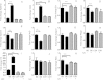

References
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman M, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Magid D, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Mussolino ME. et al. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;7:143–152. - PubMed
-
- Lusis AJ, Mar R, Pajukanta P. Genetics of atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2004;7:189–218. - PubMed
-
- Homma S, Ishii T, Malcom GT, Zieske AW, Strong JP, Tsugane S, Hirose N. Histopathological modifications of early atherosclerotic lesions by risk factors–findings in PDAY subjects. Atherosclerosis. 2001;7:389–399. - PubMed
-
- Yan ZQ, Hansson GK. Innate immunity, macrophage activation, and atherosclerosis. Immunol Rev. 2007;7:187–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

