Nontuberculous mycobacterial infection in a clinical presentation of Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome: a case report with multigene diagnostic approach
- PMID: 25115526
- PMCID: PMC4141662
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6874-14-95
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infection in a clinical presentation of Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome: a case report with multigene diagnostic approach
Abstract
Background: Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (FHCS) is caused by inflammation of perihepatic capsules associated with pelvic inflammatory disease. In recent years, infections with nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) have been increasingly occurring in immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. However, NTM has never been reported in patients with FHCS. We present the first case of a patient with extrapulmonary NTM infection in a clinical presentation of FHCS.
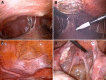
Case presentation: A 26-year-old Korean woman presented with right upper quadrant and suprapubic pain. She was initially suspected to have FHCS. However, she was refractory to conventional antibiotic therapy. Laparoscopy revealed multiple violin-string adhesions of the parietal peritoneum to the liver and miliary-like nodules on the peritoneal surfaces. Diagnosis of NTM was confirmed by the polymerase chain reaction analysis results of biopsy specimens that showed caseating granulomas with positive acid-fast bacilli. Treatment with anti-NTM medications was initiated, and the patient's symptoms were considerably ameliorated.
Conclusions: An awareness of NTM as potential pathogens, even in previously healthy adults, and efforts to exclude other confounding diseases are important to establish the diagnosis of NTM disease. NTM infection can cause various clinical manifestations, which in the present case, overlapped with the symptoms of perihepatic inflammation seen in FHCS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome associated with tuberculous salpingitis and peritonitis: a case presentation and review of literature.BMC Gastroenterol. 2018 Mar 20;18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12876-018-0768-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29558895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome in a man positive for Chlamydia trachomatis.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug;11(4):338-342. doi: 10.1007/s12328-018-0829-5. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29417387 Review.
-
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome in a male patient due to urinary tract infection.Clin Imaging. 2015 Sep-Oct;39(5):917-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Clin Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25986163
-
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome: three cases confirmed by laparoscopy.Asia Oceania J Obstet Gynaecol. 1990 Jun;16(2):105-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.1990.tb00010.x. Asia Oceania J Obstet Gynaecol. 1990. PMID: 2143066
-
An Uncommon Manifestation of Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome with Right-side Chest Pain.Acta Med Okayama. 2016;70(2):145-9. doi: 10.18926/AMO/54194. Acta Med Okayama. 2016. PMID: 27094840
Cited by
-
A rare case of miliary tuberculosis accompanying perihepatitis.Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2019 Sep;6(3):264-267. doi: 10.15441/ceem.18.017. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 30743325 Free PMC article.
-
18 F-FDG PET-CT in Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome.World J Nucl Med. 2022 Jun 23;21(2):166-168. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1750342. eCollection 2022 Jun. World J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 35865150 Free PMC article.
-
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome Consequent to a Wound Infection Following Removal of a Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter.Perit Dial Int. 2016 11-12;36(6):693-695. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2015.00292. Perit Dial Int. 2016. PMID: 27903855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peter NG, Clark LR, Jaeger JR. Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome: a diagnosis to consider in women with right upper quadrant pain. Cleve Clin J Med. 2004;71(3):233–239. - PubMed
-
- Tortoli E. Clinical manifestations of nontuberculous mycobacteria infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009;15(10):906–910. - PubMed
-
- Chetchotisakd P, Kiertiburanakul S, Mootsikapun P, Assanasen S, Chaiwarith R, Anunnatsiri S. Disseminated nontuberculous mycobacterial infection in patients who are not infected with HIV in Thailand. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(4):421–427. - PubMed
-
- Lai CC, Lee LN, Ding LW, Yu CJ, Hsueh PR, Yang PC. Emergence of disseminated infections due to nontuberculous mycobacteria in non-HIV-infected patients, including immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients in a university hospital in Taiwan. J Infect. 2006;53(2):77–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

