Invertebrate extracellular phagocyte traps show that chromatin is an ancient defence weapon
- PMID: 25115909
- PMCID: PMC4143918
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5627
Invertebrate extracellular phagocyte traps show that chromatin is an ancient defence weapon
Abstract
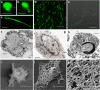
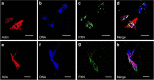
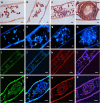
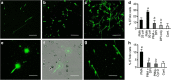
Controlled release of chromatin from the nuclei of inflammatory cells is a process that entraps and kills microorganisms in the extracellular environment. Now termed ETosis, it is important for innate immunity in vertebrates. Paradoxically, however, in mammals, it can also contribute to certain pathologies. Here we show that ETosis occurs in several invertebrate species, including, remarkably, an acoelomate. Our findings reveal that the phenomenon is primordial and predates the evolution of the coelom. In invertebrates, the released chromatin participates in defence not only by ensnaring microorganisms and externalizing antibacterial histones together with other haemocyte-derived defence factors, but crucially, also provides the scaffold on which intact haemocytes assemble during encapsulation; a response that sequesters and kills potential pathogens infecting the body cavity. This insight into the early origin of ETosis identifies it as a very ancient process that helps explain some of its detrimental effects in mammals.
Figures


References
-
- Brinkmann V. et al.. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303, 1532–1535 (2004). - PubMed
-
- von Kockritz-Blickwede M. et al.. Phagocytosis independent antimicrobial activity of mast cells by means of extracellular trap formation. Blood 111, 3070–3080 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Yousefi S. et al.. Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat. Med. 14, 949–953 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

