Transforming growth factor alpha is a critical mediator of radiation lung injury
- PMID: 25117621
- PMCID: PMC4169125
- DOI: 10.1667/RR13625.1
Transforming growth factor alpha is a critical mediator of radiation lung injury
Abstract
Radiation fibrosis of the lung is a late toxicity of thoracic irradiation. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) signaling has previously been implicated in radiation lung injury. We hypothesized that TGF-α, an EGF receptor ligand, plays a key role in radiation-induced fibrosis in lung. Mice deficient in transforming growth factor (TGF-α(-/-)) and control C57Bl/6J (C57-WT) mice were exposed to thoracic irradiation in 5 daily fractions of 6 Gy. Cohorts of mice were followed for survival (n ≥ 5 per group) and tissue collection (n = 3 per strain and time point). Collagen accumulation in irradiated lungs was assessed by Masson's trichrome staining and analysis of hydroxyproline content. Cytokine levels in lung tissue were assessed with ELISA. The effects of TGF-α on pneumocyte and fibroblast proliferation and collagen production were analyzed in vitro. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) expression and activity were measured in vitro and in vivo. Irradiated C57-WT mice had a median survival of 24.4 weeks compared to 48.2 weeks for irradiated TGF-α(-/-) mice (P = 0.001). At 20 weeks after irradiation, hydroxyproline content was markedly increased in C57-WT mice exposed to radiation compared to TGF-α(-/-) mice exposed to radiation or unirradiated C57-WT mice (63.0, 30.5 and 37.6 μg/lung, respectively, P = 0.01). C57-WT mice exposed to radiation had dense foci of subpleural fibrosis at 20 weeks after exposure, whereas the lungs of irradiated TGF-α (-/-) mice were largely devoid of fibrotic foci. Lung tissue concentrations of IL-1β, IL-4, TNF-α, TGF-β and EGF at multiple time points after irradiation were similar in C57-WT and TGF-α(-/-) mice. TGF-α in lung tissue of C57-WT mice rose rapidly after irradiation and remained elevated through 20 weeks. TGF-α(-/-) mice had lower basal LOX expression than C57-WT mice. Both LOX expression and LOX activity were increased after irradiation in all mice but to a lesser degree in TGF-α(-/-) mice. Treatment of NIH-3T3 fibroblasts with TGF-α resulted in increases in proliferation, collagen production and LOX activity. These studies identify TGF-α as a critical mediator of radiation-induced lung injury and a novel therapeutic target in this setting. Further, these data implicate TGF-α as a mediator of collagen maturation through a TGF-β independent activation of lysyl oxidase.
Figures

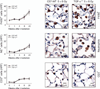
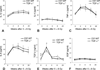

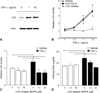

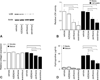
Similar articles
-
Truncated Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Protein Protects From Pulmonary Fibrosis Mediated by Irradiation in a Murine Model.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Apr 1;94(5):1163-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.11.044. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 26883561 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent induction of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in the lung tissue of fibrosis-prone mice after thoracic irradiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000 Jul 1;47(4):1033-42. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(00)00482-x. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000. PMID: 10863076
-
Interleukin-13 Receptor Subunit Alpha 2 Induces Chemokine Expression and Macrophage Polarization to Promote Inflammation and Fibrosis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2025 Apr 1;121(5):1258-1270. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.11.103. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2025. PMID: 39672516
-
Effects of lipopolysaccharide on the response of C57BL/6J mice to whole thorax irradiation.Radiother Oncol. 2012 Dec;105(3):341-9. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Radiother Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22985778 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese [correction of Magnesium] superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) plasmid/liposome pulmonary radioprotective gene therapy: modulation of irradiation-induced mRNA for IL-I, TNF-alpha, and TGF-beta correlates with delay of organizing alveolitis/fibrosis.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999;5(4):204-14. doi: 10.1053/bbmt.1999.v5.pm10465100. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999. PMID: 10465100
Cited by
-
Portrait of inflammatory response to ionizing radiation treatment.J Inflamm (Lond). 2015 Feb 18;12:14. doi: 10.1186/s12950-015-0058-3. eCollection 2015. J Inflamm (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25705130 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent DNA damage is associated with persistent injury in progressive radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Int J Radiat Biol. 2018 Dec;94(12):1104-1115. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2018.1516907. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Radiat Biol. 2018. PMID: 30238842 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of disease progression and resolution in a transgenic mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):L488-L499. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00458.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28130263 Free PMC article.
-
Lysyl Oxidase Isoforms and Potential Therapeutic Opportunities for Fibrosis and Cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016 Aug;20(8):935-45. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1151003. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016. PMID: 26848785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of both the expression and serum levels of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor β1 genes in COVID-19.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9771. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92304-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40118922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trott KR, Herrmann T, Kasper M. Target cells in radiation pneumopathy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;58:463–469. - PubMed
-
- Repertinger SK, Campagnaro E, Fuhrman J, El-Abaseri T, Yuspa SH, Hansen LA. EGFR enhances early healing after cutaneous incisional wounding. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123:982–989. - PubMed
-
- Harada C, Kawaguchi T, Ogata-Suetsugu S, Yamada M, Hamada N, Maeyama T, et al. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition worsens acute lung injury in mice with repairing airway epithelium. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:743–751. - PubMed
-
- Block ER, Matela AR, SundarRaj N, Iszkula ER, Klarlund JK. Wounding induces motility in sheets of corneal epithelial cells through loss of spatial constraints: role of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:24307–24312. - PubMed
-
- Puddicombe SM, Polosa R, Richter A, Krishna MT, Howarth PH, Holgate ST, et al. Involvement of the epidermal growth factor receptor in epithelial repair in asthma. FASEB J. 2000;14:1362–1274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

