Methylthioadenosine reprograms macrophage activation through adenosine receptor stimulation
- PMID: 25117662
- PMCID: PMC4130577
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104210
Methylthioadenosine reprograms macrophage activation through adenosine receptor stimulation
Abstract
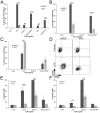
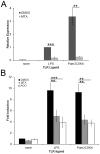
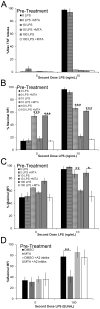
Regulation of inflammation is necessary to balance sufficient pathogen clearance with excessive tissue damage. Central to regulating inflammation is the switch from a pro-inflammatory pathway to an anti-inflammatory pathway. Macrophages are well-positioned to initiate this switch, and as such are the target of multiple therapeutics. One such potential therapeutic is methylthioadenosine (MTA), which inhibits TNFα production following LPS stimulation. We found that MTA could block TNFα production by multiple TLR ligands. Further, it prevented surface expression of CD69 and CD86 and reduced NF-KB signaling. We then determined that the mechanism of this action by MTA is signaling through adenosine A2 receptors. A2 receptors and TLR receptors synergized to promote an anti-inflammatory phenotype, as MTA enhanced LPS tolerance. In contrast, IL-1β production and processing was not affected by MTA exposure. Taken together, these data demonstrate that MTA reprograms TLR activation pathways via adenosine receptors to promote resolution of inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Lee MS, Kim YJ (2007) Signaling pathways downstream of pattern-recognition receptors and their cross talk. Annual review of biochemistry 76: 447–480. - PubMed
-
- Marzio R, Jirillo E, Ransijn A, Mauel J, Corradin SB (1997) Expression and function of the early activation antigen CD69 in murine macrophages. Journal of leukocyte biology 62: 349–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

