Effects of the racket polar moment of inertia on dominant upper limb joint moments during tennis serve
- PMID: 25117871
- PMCID: PMC4130553
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104785
Effects of the racket polar moment of inertia on dominant upper limb joint moments during tennis serve
Abstract
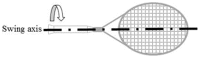
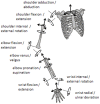
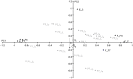
This study examined the effect of the polar moment of inertia of a tennis racket on upper limb loading in the serve. Eight amateur competition tennis players performed two sets of 10 serves using two rackets identical in mass, position of center of mass and moments of inertia other than the polar moment of inertia (0.00152 vs 0.00197 kg.m2). An eight-camera motion analysis system collected the 3D trajectories of 16 markers, located on the thorax, upper limbs and racket, from which shoulder, elbow and wrist net joint moments and powers were computed using inverse dynamics. During the cocking phase, increased racket polar moment of inertia was associated with significant increases in the peak shoulder extension and abduction moments, as well the peak elbow extension, valgus and supination moments. During the forward swing phase, peak wrist extension and radial deviation moments significantly increased with polar moment of inertia. During the follow-through phase, the peak shoulder adduction, elbow pronation and wrist external rotation moments displayed a significant inverse relationship with polar moment of inertia. During the forward swing, the magnitudes of negative joint power at the elbow and wrist were significantly larger when players served using the racket with a higher polar moment of inertia. Although a larger polar of inertia allows players to better tolerate off-center impacts, it also appears to place additional loads on the upper extremity when serving and may therefore increase injury risk in tennis players.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Joint Kinetics to Assess the Influence of the Racket on a Tennis Player's Shoulder.J Sports Sci Med. 2013 Jun 1;12(2):259-66. eCollection 2013. J Sports Sci Med. 2013. PMID: 24149804 Free PMC article.
-
Upper limb joint kinetic analysis during tennis serve: Assessment of competitive level on efficiency and injury risks.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014 Aug;24(4):700-7. doi: 10.1111/sms.12043. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014. PMID: 23293868
-
Effect of hammer mass on upper extremity joint moments.Appl Ergon. 2017 Apr;60:231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 11. Appl Ergon. 2017. PMID: 28166882
-
Long-axis rotation: the missing link in proximal-to-distal segmental sequencing.J Sports Sci. 2000 Apr;18(4):247-54. doi: 10.1080/026404100364983. J Sports Sci. 2000. PMID: 10824641 Review.
-
Shoulder muscle recruitment patterns and related biomechanics during upper extremity sports.Sports Med. 2009;39(7):569-90. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200939070-00004. Sports Med. 2009. PMID: 19530752 Review.
Cited by
-
There is no rush to upgrade the tennis racket in young intermediate competitive players: The effects of scaling racket on serve biomechanics and performance.Front Psychol. 2023 Feb 10;14:1104146. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1104146. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36844270 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive use of interaction torque during arm reaching movement from the optimal control viewpoint.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 12;6:38845. doi: 10.1038/srep38845. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27941920 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Contributors for Shoulder Injuries Among Adolescent Tennis Participants: A Prospective Group Study.Orthop J Sports Med. 2025 Jul 14;13(7):23259671251351322. doi: 10.1177/23259671251351322. eCollection 2025 Jul. Orthop J Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40666380 Free PMC article.
-
Wrist Injuries in Tennis Players: A Narrative Review.Sports Med. 2017 May;47(5):857-868. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0630-x. Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 27699697 Review.
-
Identifying the Inertial Properties of a Padel Racket: An Experimental Maneuverability Proposal.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;22(23):9266. doi: 10.3390/s22239266. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kotze J, Mitchell SR, Rothberg SJ (2000) The role of the racket in high-speed tennis serves. Sports Eng 3: 67–84.
-
- Cross R (2001) Customising a tennis racket by adding weight. Sports Eng 4: 1–14.
-
- Creveaux T, Dumas R, Chèze L, Macé P, Rogowski I (2013) Influence of racket polar moment on joint loads during tennis forehand drive. Comput Meth Biomech Biomed Eng 16: S99–101. - PubMed
-
- Morris M, Jobe F, Perry J, Pink M, Healy B (1989) Electromyographic analysis of elbow function in tennis players. Am J Sports Med 17: 241–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

