Regulation of microRNA function in somatic stem cell proliferation and differentiation
- PMID: 25118717
- PMCID: PMC4377327
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3854
Regulation of microRNA function in somatic stem cell proliferation and differentiation
Abstract
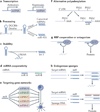
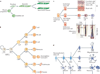
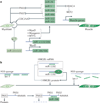
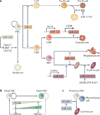
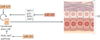
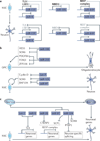
microRNAs (miRNAs) are important modulators of development. Owing to their ability to simultaneously silence hundreds of target genes, they have key roles in large-scale transcriptomic changes that occur during cell fate transitions. In somatic stem and progenitor cells--such as those involved in myogenesis, haematopoiesis, skin and neural development--miRNA function is carefully regulated to promote and stabilize cell fate choice. miRNAs are integrated within networks that form both positive and negative feedback loops. Their function is regulated at multiple levels, including transcription, biogenesis, stability, availability and/or number of target sites, as well as their cooperation with other miRNAs and RNA-binding proteins. Together, these regulatory mechanisms result in a refined molecular response that enables proper cellular differentiation and function.
Figures
References
-
- Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nature Rev. GMo. Cell Biol. 2014;15:509–524. - PubMed
-
- Babiarz JE, Blelloch R. Small RNAs – their biogenesis, regulation and function in embryonic stem cells. StemBook. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, et al. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nature Genet. 2003;35:215–217. - PubMed
-
- Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nature Rev. Genet. 2011;12:99–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

