Impaired cell death and mammary gland involution in the absence of Dock1 and Rac1 signaling
- PMID: 25118935
- PMCID: PMC4454313
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.338
Impaired cell death and mammary gland involution in the absence of Dock1 and Rac1 signaling
Abstract
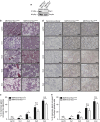
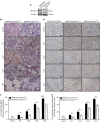
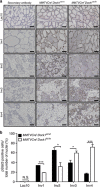
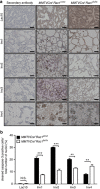
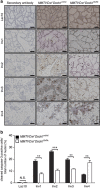
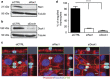
Throughout life, the tight equilibrium between cell death and the prompt clearance of dead corpses is required to maintain a proper tissue homeostasis and prevent inflammation. Following lactation, mammary gland involution is triggered and results in the death of excessive epithelial cells that are rapidly cleared by phagocytes to ensure that the gland returns to its prepregnant state. Orthologs of Dock1 (dedicator of cytokinesis 1), Elmo and Rac1 (ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1) in Caenorhabditis elegans are part of a signaling module in phagocytes that is linking apoptotic cell recognition to cytoskeletal reorganization required for engulfment. In mammals, Elmo1 was shown to interact with the phosphatidylserine receptor Bai1 and relay signals to promote phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Still, the role of the RacGEF Dock1 in the clearance of dying cells in mammals was never directly addressed. We generated two mouse models with conditional inactivation of Dock1 and Rac1 and revealed that the expression of these genes is not essential in the mammary gland during puberty, pregnancy and lactation. We induced mammary gland involution in these mice to investigate the role of Dock1/Rac1 signaling in the engulfment of cell corpses. Unpredictably, activation of Stat3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3), a key regulator of mammary gland involution, was impaired in the absence of Rac1 and Dock1 expression. Likewise, failure to activate properly Stat3 was coinciding with a significant delay in the initiation and progression of mammary gland involution in mutant animals. By using an in vitro phagocytosis assay, we observed that Dock1 and Rac1 are essential to mediate engulfment in epithelial phagocytes. In vivo, cell corpses accumulated at late time points of involution in Dock1 and Rac1 mutant mammary glands. Overall, our study demonstrated an unsuspected role for Dock1/Rac1 signaling in the initiation of mammary gland involution, and also suggested a role for this pathway in the clearance of dead cells by epithelial phagocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Reddien PW, Horvitz HR. The engulfment process of programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:193–221. - PubMed
-
- Albert ML, Kim JI, Birge RB. alphavbeta5 integrin recruits the CrkII–Dock180–rac1 complex for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:899–905. - PubMed
-
- Gumienny TL, Brugnera E, Tosello-Trampont AC, Kinchen JM, Haney LB, Nishiwaki K, et al. CED-12/ELMO, a novel member of the CrkII/Dock180/Rac pathway, is required for phagocytosis and cell migration. Cell. 2001;107:27–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

