Detrimental effects of Notch1 signaling activated by cadmium in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells
- PMID: 25118938
- PMCID: PMC4454314
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.339
Detrimental effects of Notch1 signaling activated by cadmium in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
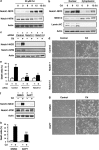
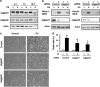
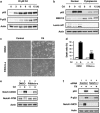
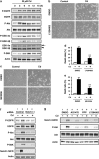
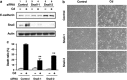
We examined the roles of Notch1 signaling and its cross-talk with other signaling pathways, including p53 and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt, in cadmium-induced cellular damage in HK-2 human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Following exposure to cadmium chloride (CdCl2), the level of Notch intracellular domain (NICD), the cleaved form of the Notch1 receptor, was increased and accumulated in the nuclear fraction. Knockdown of Notch1 with siRNA or treatment with the γ-secretase inhibitor, DAPT (N-[N-(3,5-difluorophenacetyl-L-alanyl)]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester), prevented CdCl2-induced morphological change of HK-2 cells and reduction of cell viability. Knockdown of Jagged1 or Jagged2, the ligands of the Notch1 receptor, partially suppressed cadmium cytotoxicity. Inhibition of p53 activity with pifithrin-α or inhibition of PI3K with LY294002 suppressed CdCl2-induced cellular damage and elevation of Notch1-NICD. In addition, treatment with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor, AG1478, and the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor, PPP, suppressed both Notch1-NICD accumulation and Akt phosphorylation in HK-2 cells exposed to CdCl2. However, knockdown of Notch1 did not affect CdCl2-induced p53 accumulation and phosphorylation but suppressed phosphorylation of EGFR, Akt, and p70 S6 kinase. Depletion of Notch1 suppressed CdCl2-induced reduction of E-cadherin expression and elevation of Snail expression. Furthermore, treatment with SB216763, an inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3, suppressed the potency of LY294002 treatment to reduce Snail expression in HK-2 cells exposed to CdCl2. Knockdown of Snail with siRNA partially prevented HK-2 cells from CdCl2-induced reduction of E-cadherin expression and cellular damage. These results suggest that cadmium exposure induces the activation of Notch1 signaling in renal proximal tubular cells with cooperative activation by the p53 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways; the resultant expression of Snail, a repressor of E-cadherin expression, might lead to cellular damage by decreasing cell-cell adhesion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PI3K signaling mediates diverse regulation of ATF4 expression for the survival of HK-2 cells exposed to cadmium.Arch Toxicol. 2014 Feb;88(2):403-14. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1129-y. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Arch Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24057571
-
Phosphorylation of FOXO3a by PI3K/Akt pathway in HK-2 renal proximal tubular epithelial cells exposed to cadmium.Arch Toxicol. 2013 Dec;87(12):2119-27. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1077-6. Epub 2013 May 15. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23673518
-
Hypoxia-induced down-regulation of microRNA-34a promotes EMT by targeting the Notch signaling pathway in tubular epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030771. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363487 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Curr Mol Med. 2014 May;14(4):523-34. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140331230411. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24694299 Review.
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of ARNT-regulated BIRC3 as the target factor in cadmium renal toxicity.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 11;7(1):17287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17494-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29229987 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of ferroportin expression by cadmium stimulates proliferation, EMT, and migration in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 1;356:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30030096 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the PI3K/Akt/mTor pathway using 31P-NMR spectroscopy: routes to glycogen synthase kinase 3.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 4;6:36544. doi: 10.1038/srep36544. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27811956 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of ALK4/5 signaling suppresses cadmium- and erastin-induced cell death in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells via distinct signaling mechanisms.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Nov;26(11):2371-2385. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0307-8. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30804470 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress eIF2α-ATF4 pathway-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction regulates cadmium-induced autophagy in kidney.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 2;7(6):e2251. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.78. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27253415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nordberg GF, Nogawa K, Nordberg M, Friberg LT.CadmiumIn: Nordberg GF, Fowler BA, Nordberg M, Friberg LT, (eds).Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA; 2007445–486.
-
- Prozialeck WC, Lamar PC, Lynch SM. Cadmium alters the localization of N-cadherin, E-cadherin, and β-catenin in the proximal tubule epithelium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003;189:180–195. - PubMed
-
- Prozialeck WC, Niewenhuis RJ. Cadmium (Cd2+) disrupts Ca2+-dependent cell-cell junctions and alters the pattern of E-cadherin immunofluorescence in LLC-PK1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;181:1118–1124. - PubMed
-
- Edwards JR, Kolman K, Lamar PC, Chandar N, Fay MJ, Prozialeck WC. Effects of cadmium on the sub-cellular localization of β-catenin and β-catenin-regulated gene expression in NRK-52E cells. Biometals. 2013;26:33–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

