The effect of the Ras homolog gene family (Rho), member A/Rho associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase pathway in atrial fibrosis of type 2 diabetes in rats
- PMID: 25120610
- PMCID: PMC4113648
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1843
The effect of the Ras homolog gene family (Rho), member A/Rho associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase pathway in atrial fibrosis of type 2 diabetes in rats
Abstract
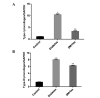
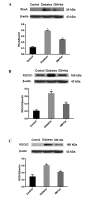
Diabetes mellitus promotes atrial structural remodeling, thereby producing atrial arrhythmogenicity. Atrial arrhythmia can substantially increase the risk of premature death. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of Ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA)/Rho associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase (ROCK) in atrial fibrosis in diabetic hearts, and the effects of fasudil hydrochloride hydrate on atrial fibrosis. An eight-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rat model of type 2 diabetes was established using a high-fat diet combined with streptozotocin [30 mg/kg, once, intraperitoneal (i.p.)]. Animals were randomly divided into three groups: Control rats, untreated diabetic rats that received vehicle, and treated diabetic rats that received Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil hydrochloride hydrate (10 mg/kg/day, i.p., for 14 weeks). The morphological features of atrial fibrosis were observed using Masson staining. The mRNA expression levels of RhoA, ROCK1, ROCK2, type-I and type-III procollagen were assessed with quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The protein levels of RhoA, ROCK1 and ROCK2 were evaluated using western blot analysis. The atria of untreated diabetic rats showed evident atrial fibrosis as compared to the control rats; the mRNA expression levels of RhoA, ROCK1, ROCK2, type-I and type-III procollagen were upregulated; and the protein levels of RhoA, ROCK1 and ROCK2 were increased. The treatment with fasudil hydrochloride hydrate significantly reduced atrial fibrosis, mRNA levels of RhoA, ROCK1, ROCK2, type-I and type-III procollagen, and the protein levels of RhoA, ROCK1 and ROCK2. The results suggested that RhoA/ROCK was involved in atrial fibrosis, and that fasudil hydrochloride hydrate ameliorates atrial fibrosis through the RhoA/ROCK pathway in rats with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Ras homolog gene family; atrial arrhythmogenicity; atrial fibrosis; fasudil; member A (RhoA)/Rho associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in rats with type 2 diabetes.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(2):225-31. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 24438608
-
Involvement of RhoA/ROCK in myocardial fibrosis in a rat model of type 2 diabetes.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Aug;32(8):999-1008. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.54. Epub 2011 Jul 11. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 21743486 Free PMC article.
-
Nonylphenol exposure induces myocardial fibrosis via the RhoA/ROCK1/MLC-signaling pathway.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025 Jul 1;299:118423. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.118423. Epub 2025 May 29. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025. PMID: 40446736
-
The Physiology, Pathology, and Therapeutic Interventions for ROCK Isoforms in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 25;11:585633. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.585633. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33101039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho Kinases and Cardiac Remodeling.Circ J. 2016 Jun 24;80(7):1491-8. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-16-0433. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Circ J. 2016. PMID: 27251065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concomitant Diabetes and Atrial Fibrillation: Epicardial Fat and Macrophage-Related Mechanisms.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2025 Jul;41(5):e70065. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.70065. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 40587764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Verification of Potential Therapeutic Target Genes in Berberine-Treated Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats through Bioinformatics Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 15;11(11):e0166378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166378. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27846294 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Diabetes Induces Prolonged P-wave Duration without Left Atrial Enlargement.J Korean Med Sci. 2016 Apr;31(4):525-34. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.525. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Korean Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27051235 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin restores electrophysiology of small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in the atrium of GK diabetic rats.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Apr 10;18(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0805-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29636010 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling pathways with Dietary Phytocompounds and repurposed drug combinations for overcoming drug resistance in various cancers.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 23;11(3):e41964. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41964. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39959483 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kato T, Yamashita T, Sekiguchi A, et al. What are arrhythmogenic substrates in diabetic rat atria? J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17:890–894. - PubMed
-
- Shimokawa H, Takeshita A. Rho-kinase is an important therapeutic target in cardiovascular medicine. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1767–1775. - PubMed
-
- Shimokawa H. Rho-kinase as a novel therapeutic target in treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2002;39:319–327. - PubMed
-
- Rolfe BE, Worth NF, World CJ, et al. Rho and vascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 2005;183:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Tapia PC. RhoA, Rho kinase, JAK2, and STAT3 may be the intracellular determinants of longevity implicated in the progeric influence of obesity: Insulin, IGF-1, and leptin may all conspire to promote stem cell exhaustion. Med Hypotheses. 2006;66:570–576. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
