Performing chest x-rays at inspiration in uncooperative children: the effect of exercises with a training program for radiology technicians
- PMID: 25120930
- PMCID: PMC4120922
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/312846
Performing chest x-rays at inspiration in uncooperative children: the effect of exercises with a training program for radiology technicians
Abstract
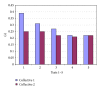
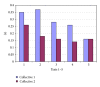
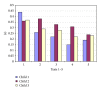
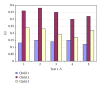
Objective. It is difficult to acquire a chest X-ray of a crying infant at maximum inspiration. A computer program was developed for technician training. Method. Video clips of 3 babies were used and the moment of deepest inspiration was determined in the single-frame view. 12 technicians simulated chest radiographs at normal video speed by pushing a button. The computer program stopped the video and calculated the period of time to the optimal instant for a chest X-ray. Demonstration software can be tested at website online. Every technician simulated 10 chest X-rays for each of the 3 video clips. The technicians then spent 40 minutes practicing performing chest X-rays at optimal inspiration. The test was repeated after 5, 20, and 40 minutes of practice. Results. 6 participants showed a significant improvement after exercises (collective 1). Deviation from the optimal instant for taking an X-ray at inspiration decreased from 0.39 to 0.22 s after 40 min of practice. 6 technicians showed no significant improvement (collective 2). Deviation decreased from a low starting value of 0.25 s to 0.21 s. Conclusion. The tested computer program improves the ability of radiology technicians to take a chest X-ray at optimal inspiration in a crying child.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Training program for radiologic technologists for performing chest X-rays at inspiration in uncooperative children].Rofo. 2009 Mar;181(3):237-41. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109142. Epub 2009 Feb 19. Rofo. 2009. PMID: 19229789 German.
-
[Radiation exposure of children in pediatric radiology. Part 4: Entrance doses achieved during the X-ray examination of the chest].Rofo. 2008 Dec;180(12):1082-103. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1027787. Epub 2008 Nov 13. Rofo. 2008. PMID: 19009497 German.
-
Family medicine residents' skill levels in emergency chest X-ray interpretation.BMC Fam Pract. 2021 Feb 17;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12875-021-01390-3. BMC Fam Pract. 2021. PMID: 33596838 Free PMC article.
-
Credentialing of pharmacy technicians in the USA.Int J Pharm Pract. 2011 Aug;19(4):219-27. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7174.2011.00095.x. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Int J Pharm Pract. 2011. PMID: 21733009 Review.
-
[Aspects of radiation protection during chest X-radiography].Radiologe. 2015 Jul;55(7):580-7. doi: 10.1007/s00117-014-2776-6. Radiologe. 2015. PMID: 26195331 Review. German.
References
-
- Alt CD, Engelmann D, Schenk JP, et al. Quality control of thoracic X-rays in children in diagnostic centers with and without pediatric-radiologic competence. Fortschr Röntgenstr. 2006;178(2):191–199. - PubMed
-
- Bramson RT, Griscom NT, Cleveland RH. Interpretation of chest radiographs in infants with cough and fever. Radiology. 2005;236(1):22–29. - PubMed
-
- Griscom NT, Wohl MEB, Kirkpatrick JA., Jr. Lower respiratory infections: how infants differ from adults. Radiologic Clinics of North America. 1978;16(3):367–387. - PubMed
-
- Langen HJ, Kohlhauser-Vollmuth C, Muras S, Stenzel M, Beer M. Training program for radiologic technologists for performing chest X-rays at inspiration in uncooperative children. Fortschr Röntgenstr. 2009;181(3):237–241. - PubMed
-
- Dunnett CW. A multiple comparison procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 1955;50(272):1096–1121.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

