Fungi treated with small chemicals exhibit increased antimicrobial activity against facultative bacterial and yeast pathogens
- PMID: 25121102
- PMCID: PMC4119895
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/540292
Fungi treated with small chemicals exhibit increased antimicrobial activity against facultative bacterial and yeast pathogens
Abstract
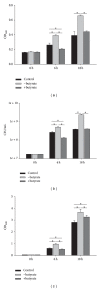
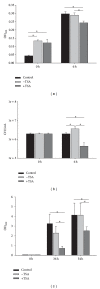
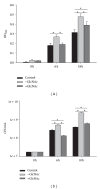
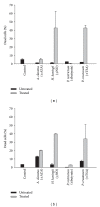
For decades, fungi have been the main source for the discovery of novel antimicrobial drugs. Recent sequencing efforts revealed a still high number of so far unknown "cryptic" secondary metabolites. The production of these metabolites is presumably epigenetically silenced under standard laboratory conditions. In this study, we investigated the effect of six small mass chemicals, of which some are known to act as epigenetic modulators, on the production of antimicrobial compounds in 54 spore forming fungi. The antimicrobial effect of fungal samples was tested against clinically facultative pathogens and multiresistant clinical isolates. In total, 30 samples of treated fungi belonging to six different genera reduced significantly growth of different test organisms compared to the untreated fungal sample (growth log reduction 0.3-4.3). For instance, the pellet of Penicillium restrictum grown in the presence of butyrate revealed significant higher antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus (S.) aureus and multiresistant S. aureus strains and displayed no cytotoxicity against human cells, thus making it an ideal candidate for antimicrobial compound discovery. Our study shows that every presumable fungus, even well described fungi, has the potential to produce novel antimicrobial compounds and that our approach is capable of rapidly filling the pipeline for yet undiscovered antimicrobial substances.
Figures

References
-
- Molinari G. Natural products in drug discovery: present status and perspectives. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2009;655:13–27. - PubMed
-
- Taylor PW. Alternative natural sources for a new generation of antibacterial agents. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 2013;42(3):195–201. - PubMed
-
- Winter JM, Behnken S, Hertweck C. Genomics-inspired discovery of natural products. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 2011;15(1):22–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

