Collateral damage: microbiota-derived metabolites and immune function in the antibiotic era
- PMID: 25121745
- PMCID: PMC4151313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.07.009
Collateral damage: microbiota-derived metabolites and immune function in the antibiotic era
Abstract
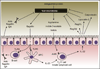
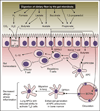
Our long-standing evolutionary association with gut-associated microbial communities has given rise to an intimate relationship, which affects many aspects of human health. Recent studies on the mechanisms that link these microbial communities to immune education, nutrition, and protection against pathogens point to microbiota-derived metabolites as key players during these microbe-host interactions. A disruption of gut-associated microbial communities by antibiotic treatment can result in a depletion of microbiota-derived metabolites, thereby enhancing pathogen susceptibility, impairing immune homeostasis, and contributing to the rise of certain chronic inflammatory diseases. Here, we highlight some of the recently elucidated mechanisms that showcase the impacts of microbiota-derived metabolites on human health.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Lahham SH, Peppelenbosch MP, Roelofsen H, Vonk RJ, Venema K. Biological effects of propionic acid in humans; metabolism, potential applications and underlying mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1801:1175–1183. - PubMed
-
- Alex S, Lange K, Amolo T, Grinstead JS, Haakonsson AK, Szalowska E, Koppen A, Mudde K, Haenen D, Al-Lahham S, Roelofsen H, Houtman R, van der Burg B, Mandrup S, Bonvin AM, Kalkhoven E, Muller M, Hooiveld GJ, Kersten S. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate angiopoietin-like 4 synthesis in human colon adenocarcinoma cells by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:1303–1316. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R25 GM056765/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T35 OD010956/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI107393/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI107393/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- OD11147/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI112241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- OD010931/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- AI112241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 OD010931/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI096528/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 OD011147/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- AI096528/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

