Distinct patterns of the lipid alterations between genotype 1 and 2 chronic hepatitis C patients after viral clearance
- PMID: 25122116
- PMCID: PMC4133245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104783
Distinct patterns of the lipid alterations between genotype 1 and 2 chronic hepatitis C patients after viral clearance
Abstract
Background: The hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype-specific impacts on the host metabolic alterations remained inconclusive.
Methods: A prospective study including 229 (118 genotype 1 (G1) and 111 G2) consecutive chronic HCV patients who had completed a course of anti-HCV treatment and underwent pre- and 24 weeks post-treatment surveys of metabolic profiles was conducted. Patients were stratified according to the therapeutic response, viral genotype and baseline insulin resistance (IR: homeostasis model assessments of IR (HOMA-IR) ≥ 2.5). Paired t-tests were used to compare the pre- and post-treatment variables.
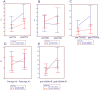
Results: Significant post-therapeutic increases in cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL, LDL, apolipoprotein A1 and apolipoprotein B were observed in patients with sustained virological response (SVR) but not in those without. Among those with SVR, post-therapeutic increases in HDL (p<0.001) and apolipoprotein A1 (p = 0.012) were only found in G2, whereas increased triglyceride/HDL (p = 0.01) ratios were only found in G1 patients. When stratified by baseline IR among those with SVR, a significant increase in post-treatment HDL (p = 0.019) and apolipoprotein A1 (p = 0.012) but a decrease in HOMA-IR (p = 0.04), C-peptide (p = 0.019) and hemoglobin A1c (p = 0.047) were found in patients with baseline IR; a significant increase in HOMA-IR (p = 0.002) was found in patients without baseline IR. The latter change was observed only in G1 (p = 0.01) but not G2 patients. Although the pre-treatment metabolic profiles of G1 and G2 patients were indifferent, G1 had higher post-treatment triglyceride/HDL ratios (p = 0.041) and triglyceride (p = 0.044) levels than G2 patients.
Conclusions: G2 benefit more than G1 patients from viral clearance in metabolic alterations, particularly in those without baseline IR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Negro F (2010) Abnormalities of lipid metabolism in hepatitis C virus infection. Gut 59: 1279–1287. - PubMed
-
- Simmonds P, Bukh J, Combet C, Deléage G, Enomoto N, et al. (2005) Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 42: 962–73. - PubMed
-
- Negro F (2006) Insulin resistance and HCV: will new knowledge modify clinical management? J Hepatol 45: 514–9. - PubMed
-
- Huang CF, Yeh ML, Huang JF, Yang JF, Hsieh MY, et al. (2012) Host interleukin-28B genetic variants versus viral kinetics in determining responses to standard-of-care for Asians with hepatitis C genotype 1. Antiviral Res 93: 239–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources