Global genetic variations predict brain response to faces
- PMID: 25122193
- PMCID: PMC4133042
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004523
Global genetic variations predict brain response to faces
Erratum in
- PLoS Genet. 2014 Oct;10(10):e1004802
Abstract
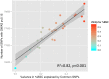
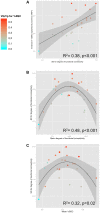
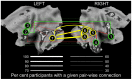
Face expressions are a rich source of social signals. Here we estimated the proportion of phenotypic variance in the brain response to facial expressions explained by common genetic variance captured by ∼ 500,000 single nucleotide polymorphisms. Using genomic-relationship-matrix restricted maximum likelihood (GREML), we related this global genetic variance to that in the brain response to facial expressions, as assessed with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in a community-based sample of adolescents (n = 1,620). Brain response to facial expressions was measured in 25 regions constituting a face network, as defined previously. In 9 out of these 25 regions, common genetic variance explained a significant proportion of phenotypic variance (40-50%) in their response to ambiguous facial expressions; this was not the case for angry facial expressions. Across the network, the strength of the genotype-phenotype relationship varied as a function of the inter-individual variability in the number of functional connections possessed by a given region (R(2) = 0.38, p<0.001). Furthermore, this variability showed an inverted U relationship with both the number of observed connections (R2 = 0.48, p<0.001) and the magnitude of brain response (R(2) = 0.32, p<0.001). Thus, a significant proportion of the brain response to facial expressions is predicted by common genetic variance in a subset of regions constituting the face network. These regions show the highest inter-individual variability in the number of connections with other network nodes, suggesting that the genetic model captures variations across the adolescent brains in co-opting these regions into the face network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Toh WL (2011) Current visual scanpath research: a review of investigations into the psychotic, anxiety, and mood disorders. Compr Psychiatry 52: 567–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

