The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis
- PMID: 25122198
- PMCID: PMC4409786
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-1010
The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis
Abstract
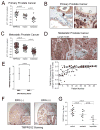
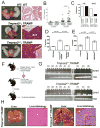
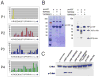
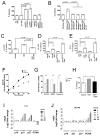
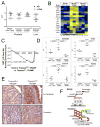
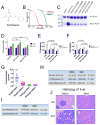
TMPRSS2 is an androgen-regulated cell-surface serine protease expressed predominantly in prostate epithelium. TMPRSS2 is expressed highly in localized high-grade prostate cancers and in the majority of human prostate cancer metastases. Through the generation of mouse models with a targeted deletion of Tmprss2, we demonstrate that the activity of this protease regulates cancer cell invasion and metastasis to distant organs. By screening combinatorial peptide libraries, we identified a spectrum of TMPRSS2 substrates that include pro-hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). HGF activated by TMPRSS2 promoted c-MET receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, and initiated a proinvasive epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype. Chemical library screens identified a potent bioavailable TMPRSS2 inhibitor that suppressed prostate cancer metastasis in vivo. Together, these findings provide a mechanistic link between androgen-regulated signaling programs and prostate cancer metastasis that operate via context-dependent interactions with extracellular constituents of the tumor microenvironment.
Significance: The vast majority of prostate cancer deaths are due to metastasis. Loss of TMPRSS2 activity dramatically attenuated the metastatic phenotype through mechanisms involving the HGF-c-MET axis. Therapeutic approaches directed toward inhibiting TMPRSS2 may reduce the incidence or progression of metastasis in patients with prostate cancer.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Prostate cancer: TMPRSS2 promotes metastasis through proteolysis.Nat Rev Urol. 2014 Oct;11(10):546. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2014.238. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Nat Rev Urol. 2014. PMID: 25179500 No abstract available.
References
-
- Netzel-Arnett S, Hooper JD, Szabo R, Madison EL, Quigley JP, Bugge TH, et al. Membrane anchored serine proteases: a rapidly expanding group of cell surface proteolytic enzymes with potential roles in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:237–58. - PubMed
-
- Hooper JD, Clements JA, Quigley JP, Antalis TM. Type II transmembrane serine proteases. Insights into an emerging class of cell surface proteolytic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:857–60. - PubMed
-
- Szabo R, Bugge TH. Type II transmembrane serine proteases in development and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40:1297–316. - PubMed
-
- Szabo R, Wu Q, Dickson RB, Netzel-Arnett S, Antalis TM, Bugge TH. Type II transmembrane serine proteases. Thromb Haemost. 2003;90:185–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

