Elevated APOBEC3B correlates with poor outcomes for estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancers
- PMID: 25123150
- PMCID: PMC4228172
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-014-0196-8
Elevated APOBEC3B correlates with poor outcomes for estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancers
Abstract
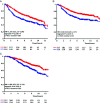
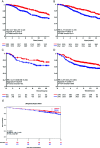
Recent observations connected DNA cytosine deaminase APOBEC3B to the genetic evolution of breast cancer. We addressed whether APOBEC3B is associated with breast cancer clinical outcomes. APOBEC3B messenger RNA (mRNA) levels were related in 1,491 primary breast cancers to disease-free (DFS), metastasis-free (MFS), and overall survival (OS). For independent validation, APOBEC3B mRNA expression was associated with patient outcome data in five additional cohorts (over 3,500 breast cancer cases). In univariate Cox regression analysis, increasing APOBEC3B expression as a continuous variable was associated with worse DFS, MFS, and OS (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.20, 1.21, and 1.24, respectively; all P < .001). Also, in untreated ER-positive (ER+), but not in ER-, lymph-node-negative patients, high APOBEC3B levels were associated with a poor DFS (continuous variable: HR = 1.29, P = .001; dichotomized at the median level, HR = 1.66, P = .0002). This implies that APOBEC3B is a marker of pure prognosis in ER + disease. These findings were confirmed in the analyses of five independent patient sets. In these analyses, APOBEC3B expression dichotomized at the median level was associated with adverse outcomes (METABRIC discovery and validation, 788 and 706 ER + cases, disease-specific survival (DSS), HR = 1.77 and HR = 1.77, respectively, both P < .001; Affymetrix dataset, 754 ER + cases, DFS, HR = 1.57, P = 2.46E-04; NKI295, 181 ER + cases, DFS, HR = 1.72, P = .054; and BIG 1-98, 1,219 ER + cases, breast-cancer-free interval (BCFI), HR = 1.42, P = 0.0079). APOBEC3B is a marker of pure prognosis and poor outcomes for ER + breast cancer, which strongly suggests that genetic aberrations induced by APOBEC3B contribute to breast cancer progression.
Conflict of interest statement
R.S.H. is co-founder of ApoGen Biotechnologies L.L.C. None the other author have anything to disclaim.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Progressive APOBEC3B mRNA expression in distant breast cancer metastases.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 31;12(1):e0171343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171343. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28141868 Free PMC article.
-
The 29.5 kb APOBEC3B Deletion Polymorphism Is Not Associated with Clinical Outcome of Breast Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 23;11(8):e0161731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161731. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27552096 Free PMC article.
-
High TWIST1 mRNA expression is associated with poor prognosis in lymph node-negative and estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer and is co-expressed with stromal as well as ECM related genes.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 11;14(5):R123. doi: 10.1186/bcr3317. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22967435 Free PMC article.
-
Unfavorable prognosis and clinical consequences of APOBEC3B expression in breast and other cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2022;44(1):153-169. doi: 10.3233/TUB-211577. Tumour Biol. 2022. PMID: 36093650
-
Molecular mechanism and clinical impact of APOBEC3B-catalyzed mutagenesis in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 21;17(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0498-3. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25848704 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Competition for DNA binding between the genome protector replication protein A and the genome modifying APOBEC3 single-stranded DNA deaminases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 28;50(21):12039-12057. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1121. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36444883 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Reactivities of 2-Furylquinolines: Ubiquitous Scaffolds in Common High-Throughput Screening Libraries.J Med Chem. 2015 Sep 24;58(18):7419-30. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00930. Epub 2015 Sep 11. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26358009 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive APOBEC3B mRNA expression in distant breast cancer metastases.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 31;12(1):e0171343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171343. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28141868 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3B Nuclear Localization Requires Two Distinct N-Terminal Domain Surfaces.J Mol Biol. 2018 Aug 17;430(17):2695-2708. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.04.044. Epub 2018 May 19. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29787764 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of APOBEC3 mutagenesis in human cancer cells.Nature. 2022 Jul;607(7920):799-807. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04972-y. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35859169 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

