Long-distance axonal growth from human induced pluripotent stem cells after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 25123310
- PMCID: PMC4144679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.07.014
Long-distance axonal growth from human induced pluripotent stem cells after spinal cord injury
Abstract
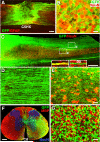
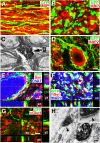
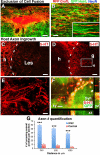
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from a healthy 86-year-old male were differentiated into neural stem cells and grafted into adult immunodeficient rats after spinal cord injury. Three months after C5 lateral hemisections, iPSCs survived and differentiated into neurons and glia and extended tens of thousands of axons from the lesion site over virtually the entire length of the rat CNS. These iPSC-derived axons extended through adult white matter of the injured spinal cord, frequently penetrating gray matter and forming synapses with rat neurons. In turn, host supraspinal motor axons penetrated human iPSC grafts and formed synapses. These findings indicate that intrinsic neuronal mechanisms readily overcome the inhibitory milieu of the adult injured spinal cord to extend many axons over very long distances; these capabilities persist even in neurons reprogrammed from very aged human cells.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Fujimoto Y, Abematsu M, Falk A, Tsujimura K, Sanosaka T, Juliandi B, Semi K, Namihira M, Komiya S, Smith A, et al. Treatment of a mouse model of spinal cord injury by transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived long-term self-renewing neuroepithelial-like stem cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30:1163–1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

