Control of Toll-like receptor-mediated T cell-independent type 1 antibody responses by the inducible nuclear protein IκB-ζ
- PMID: 25124037
- PMCID: PMC4223300
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553230
Control of Toll-like receptor-mediated T cell-independent type 1 antibody responses by the inducible nuclear protein IκB-ζ
Abstract
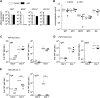
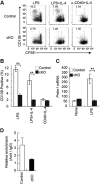
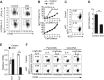
Antibody responses have been classified as being either T cell-dependent or T cell-independent (TI). TI antibody responses are further classified as being either type 1 (TI-1) or type 2 (TI-2), depending on their requirement for B cell-mediated antigen receptor signaling. Although the mechanistic basis of antibody responses has been studied extensively, it remains unclear whether different antibody responses share similarities in their transcriptional regulation. Here, we show that mice deficient in IκB-ζ, specifically in their B cells, have impaired TI-1 antibody responses but normal T cell-dependent and TI-2 antibody responses. The absence of IκB-ζ in B cells also impaired proliferation triggered by Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation, plasma cell differentiation, and class switch recombination (CSR). Mechanistically, IκB-ζ-deficient B cells could not induce TLR-mediated induction of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a class-switch DNA recombinase. Retroviral transduction of AID in IκB-ζ-deficient B cells restored CSR activity. Furthermore, acetylation of histone H3 in the vicinity of the transcription start site of the gene that encodes AID was reduced in IκB-ζ-deficient B cells relative to IκB-ζ-expressing B cells. These results indicate that IκB-ζ regulates TLR-mediated CSR by inducing AID. Moreover, IκB-ζ defines differences in the transcriptional regulation of different antibody responses.
Keywords: Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID); B Cell; Cell Differentiation; Cellular Immune Response; Immunology; IκB-z; Toll-like Receptor (TLR); Transcription Factor.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
B cell TLR1/2, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 interact in induction of class switch DNA recombination: modulation by BCR and CD40, and relevance to T-independent antibody responses.Autoimmunity. 2015 Feb;48(1):1-12. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2014.993027. Autoimmunity. 2015. PMID: 25536171 Free PMC article.
-
B cell Rab7 mediates induction of activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression and class-switching in T-dependent and T-independent antibody responses.J Immunol. 2015 Apr 1;194(7):3065-78. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401896. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25740947 Free PMC article.
-
B cell TLRs and induction of immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jun 1;17(7):2594-615. doi: 10.2741/4073. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BCR-signalling synergizes with TLR-signalling for induction of AID and immunoglobulin class-switching through the non-canonical NF-κB pathway.Nat Commun. 2012 Apr 3;3:767. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1769. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 22473011 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling control of antibody isotype switching.Adv Immunol. 2019;141:105-164. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Adv Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30904131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Modulation of Autophagy in Leukaemia and Lymphoma.Cells. 2019 Jan 30;8(2):103. doi: 10.3390/cells8020103. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30704144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Analysis of the Transcriptional Regulator IκB-ζ in Intestinal Homeostasis.Dig Dis Sci. 2022 Apr;67(4):1252-1259. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06958-8. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Dig Dis Sci. 2022. PMID: 33818662
-
IκBζ: an emerging player in cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):66310-66322. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11624. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27579619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Curcumin Analog GO-Y030 Controls the Generation and Stability of Regulatory T Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 23;12:687669. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.687669. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34248973 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical IκB protein IκB(NS) is important for Toll-like receptor-induced interleukin-10 production in B cells.Immunology. 2016 Apr;147(4):453-63. doi: 10.1111/imm.12578. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Immunology. 2016. PMID: 26749055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foy T. M., Shepherd D. M., Durie F. H., Aruffo A., Ledbetter J. A., Noelle R. J. (1993) In vivo CD40-gp39 interactions are essential for thymus-dependent humoral immunity. II. Prolonged suppression of the humoral immune response by an antibody to the ligand for CD40, gp39. J. Exp. Med. 178, 1567–1575 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van den Eertwegh A. J., Noelle R. J., Roy M., Shepherd D. M., Aruffo A., Ledbetter J. A., Boersma W. J., Claassen E. (1993) In vivo CD40-gp39 interactions are essential for thymus-dependent humoral immunity. I. In vivo expression of CD40 ligand, cytokines, and antibody production delineates sites of cognate T-B cell interactions. J. Exp. Med. 178, 1555–1565 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mosier D. E., Mond J. J., Goldings E. A. (1977) The ontogeny of thymic independent antibody responses in vitro in normal mice and mice with an X-linked B cell defect. J. Immunol. 119, 1874–1878 - PubMed
-
- Mond J. J., Lees A., Snapper C. M. (1995) T cell-independent antigens type 2. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13, 655–692 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

