Interventions to reduce haemorrhage during myomectomy for fibroids
- PMID: 25125317
- PMCID: PMC9017065
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005355.pub5
Interventions to reduce haemorrhage during myomectomy for fibroids
Abstract
Background: Benign smooth muscle tumours of the uterus, known as fibroids or myomas, are often symptomless. However, about one-third of women with fibroids will present with symptoms that are severe enough to warrant treatment. The standard treatment of symptomatic fibroids is hysterectomy (that is surgical removal of the uterus) for women who have completed childbearing, and myomectomy for women who desire future childbearing or simply want to preserve their uterus. Myomectomy, the surgical removal of myomas, can be associated with life-threatening bleeding. Excessive bleeding can necessitate emergency blood transfusion. Knowledge of the effectiveness of the interventions to reduce bleeding during myomectomy is essential to enable evidence-based clinical decisions. This is an update of the review published in The Cochrane Library (2011, Issue 11).
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness, safety, tolerability and costs of interventions to reduce blood loss during myomectomy.
Search methods: In June 2014, we conducted electronic searches in the Cochrane Menstrual Disorders and Subfertility Group Specialised Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL and PsycINFO, and trial registers for ongoing and registered trials.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that compared potential interventions to reduce blood loss during myomectomy to placebo or no treatment.
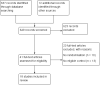
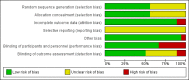
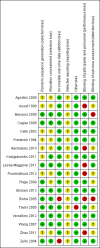
Data collection and analysis: The two authors independently selected RCTs for inclusion, assessed the risk of bias and extracted data from the included RCTs. The primary review outcomes were blood loss and need for blood transfusion. We expressed study results as mean differences (MD) for continuous data and odds ratios for dichotomous data, with 95% confidence intervals (CI). We assessed the quality of evidence using GRADE methods.
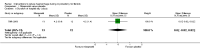
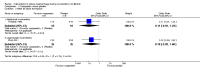
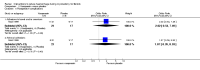
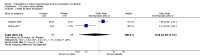
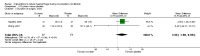
Main results: Eighteen RCTs with 1250 participants met our inclusion criteria. The studies were conducted in hospital settings in low, middle and high income countries.Blood lossWe found significant reductions in blood loss with the following interventions: vaginal misoprostol (2 RCTs, 89 women: MD -97.88 ml, 95% CI -125.52 to -70.24; I(2) = 43%; moderate-quality evidence); intramyometrial vasopressin (3 RCTs, 128 women: MD -245.87 ml, 95% CI -434.58 to -57.16; I(2) = 98%; moderate-quality evidence); intramyometrial bupivacaine plus epinephrine (1 RCT, 60 women: MD -68.60 ml, 95% CI -93.69 to -43.51; low-quality evidence); intravenous tranexamic acid (1 RCT, 100 women: MD -243 ml, 95% CI -460.02 to -25.98; low-quality evidence); gelatin-thrombin matrix (1 RCT, 50 women: MD -545.00 ml, 95% CI -593.26 to -496.74; low-quality evidence); intravenous ascorbic acid (1 RCT, 102 women: MD -411.46 ml, 95% CI -502.58 to -320.34; low-quality evidence); vaginal dinoprostone (1 RCT, 108 women: MD -131.60 ml, 95% CI -253.42 to -9.78; low-quality evidence); loop ligation of the myoma pseudocapsule (1 RCT, 70 women: MD -305.01 ml, 95% CI -354.83 to -255.19; low-quality evidence); and a fibrin sealant patch (1 RCT, 70 women: MD -26.50 ml, 95% CI -44.47 to -8.53; low-quality evidence). We found evidence of significant reductions in blood loss with a polyglactin suture (1 RCT, 28 women: MD -1870.0 ml, 95% CI -2547.16 to 1192.84) or a Foley catheter (1 RCT, 93 women: MD -240.70 ml, 95% CI -359.61 to -121.79) tied around the cervix. However, pooling data from these peri-cervical tourniquet RCTs revealed significant heterogeneity of the effects (2 RCTs, 121 women: MD (random) -1019.85 ml, 95% CI -2615.02 to 575.32; I(2) = 95%; low-quality evidence). There was no good evidence of an effect on blood loss with oxytocin, morcellation or clipping of the uterine artery.Need for blood transfusion We found significant reductions in the need for blood transfusion with vasopressin (2 RCTs, 90 women: OR 0.15, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.74; I(2) = 0%; moderate-quality evidence); peri-cervical tourniquet (2 RCTs, 121 women: OR 0.09, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.84; I(2) = 69%; low-quality evidence); gelatin-thrombin matrix (1 RCT, 100 women: OR 0.01, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.10; low-quality evidence) and dinoprostone (1 RCT, 108 women: OR 0.17, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.81; low-quality evidence), but no evidence of effect on the need for blood transfusion with misoprostol, oxytocin, tranexamic acid, ascorbic acid, loop ligation of the myoma pseudocapsule and a fibrin sealant patch.There were insufficient data on the adverse effects and costs of the different interventions.
Authors' conclusions: At present there is moderate-quality evidence that misoprostol may reduce bleeding during myomectomy, and low-quality evidence that bupivacaine plus epinephrine, tranexamic acid, gelatin-thrombin matrix, a peri-cervical tourniquet, ascorbic acid, dinoprostone, loop ligation and a fibrin sealant patch may reduce bleeding during myomectomy. There is no evidence that oxytocin, morcellation and temporary clipping of the uterine artery reduce blood loss. Further well designed studies are required to establish the effectiveness, safety and costs of different interventions for reducing blood loss during myomectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures




































































Update of
-
Interventions to reduce haemorrhage during myomectomy for fibroids.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov 9;(11):CD005355. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005355.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Aug 15;(8):CD005355. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005355.pub5. PMID: 22071823 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Agostini 2005 {published data only}
-
- Agostini A, Ronda I, Franchi F, Bretelle F, Roger V, Cravello L, et al. Oxytocin during myomectomy: a randomized study. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology 2005;118:235‐8. - PubMed
Assaf 1999 {published data only}
-
- Assaf A. Adhesions after laparoscopic myomectomy: effect of the technique used. Gynaecological Endoscopy 1999;8:225‐9.
Benassi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Benassi L, Lopopolo G, Pazzoni F, Ricci L, Kaihura C, Piazza F, et al. Chemically assisted dissection of tissues: an interesting support in abdominal myomectomy. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 2000;191:65‐9. - PubMed
Caglar 2008 {published data only}
-
- Caglar GS, Tasci Y, Kayikcioglu F, Haberal A. Intravenous tranexamic acid use in myomectomy: a prospective randomized double‐blind placebo controlled study. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology 2008;137(2):227‐31. - PubMed
Celik 2003 {published data only}
-
- Celik H, Sapmaz E. Use of a single preoperative dose of misoprostol is efficacious for patients who undergo abdominal myomectomy. Fertility and Sterility 2003;79:1207‐10. - PubMed
Frederick 1994 {published data only}
-
- Frederick J, Fletcher H, Simeon D, Mullings A, Hardie M. Intramyometrial vasopressin as a haemostatic agent during myomectomy. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1994;101:435‐7. - PubMed
Ikechebelu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ikechebelu JI, Ezeama CO, Obiechina NJ. The use of torniquet to reduce blood loss at myomectomy. Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice 2010;13(2):154‐8. - PubMed
Kalogiannidis 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kalogiannidis I, Xiromeritis P, Prapas N, Prapas Y. Intravaginal misoprostol reduces intraoperative blood loss in minimally invasive myomectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics and Gynecology 2011;38(1):46‐9. - PubMed
Leone Maggiore 2011 {published data only}
-
- Maggiore Leone Roberti U, Alessandri F, Ferrero S. Tachosil application after laparoscopic myomectomy: A prospective randomized trial [Applicazione di Tachosil dopo miomectomia laparoscopica: studio prospettico randomizzato]. Italian Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics 2011;23(4):147‐54.
Pourmatroud 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pourmatroud E, Hormozi L, Masoud H, Golshahi R. Intravenous ascobi acid (vitamin C) administration in myomectomy: a prospective, randomized, clinical trial. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;285:111‐5. - PubMed
Raga 2009 {published data only}
-
- Raga F, Sanz‐Cortes M, Bonilla F, Casan EM, Bonilla‐Musoles F. Reducing blood loss at myomectomy with use of a gelatin‐thrombin matrix hemostatic sealant. Fertility and Sterility 2009;92(1):356‐60. - PubMed
Shokeir 2013 {published data only}
-
- Shokeir T, Shalaby H, Nabil H, Barakat R. Reducing blood loss at abdominal myomectomy with preoperative use of dinoprostone intravaginal suppository: a randomized placebo‐controlled pilot study. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology 2013;166:61‐4. - PubMed
Sinha 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sinha R, Hedge A, Warty N, Mahajan C. Laparoscopic myomectomy: Enucleation of the myoma by morcellation while attached to the uterus. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 2005;12:284‐9. - PubMed
Taylor 2005 {published data only}
-
- Taylor A, Sharma M, Tsirkas P, Spiezio Sardo A, Setchell M, Magos A. Reducing blood loss at open myomectomy using triple tourniquets: a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2005;112:340‐5. - PubMed
Vercellino 2012 {published data only}
-
- Vercellino G, Erdemoglu E, Joe A, Hopfenmueller W, Holthaus B, Kohler C, Schneider A, Hasenbein K, Chiantera V. Laparoscopic temporary clipping of uterine artery during laparoscopic myomectomy. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;286(5):1181‐1186. - PubMed
Wang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wang CJ, Lee CL, Yuen LT, Kay N, Han CM, Soong YK. Oxytocin infusion in laparoscopic myomectomy may decrease operative blood loss. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 2007;14(2):184‐8. - PubMed
Zhao 2011 {published data only}
-
- Zhao F, Jiao Y, Guo Z, Hou R, Wang M. Evaluation of loop ligation of larger myoma pseudocapsule combined with vasopressin on laparoscopic myomectomy. Fertility and Sterility 2011;95(2):762‐6. - PubMed
Zullo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zullo F, Palomba S, Corea D, Pellicano M, Russo T, Falbo A, et al. Bupivacaine plus epinephrine for laparoscopic myomectomy: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2004;104:243‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alborzi 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Alborzi S, Ghannadan E, Alborzi S, Alborzi M. A comparison of combined laparoscopic uterine artery ligation and myomectomy versus laparoscopic myomectomy in treatment of symptomatic myoma. Fertility and Sterility 2009;92(2):742‐7. - PubMed
Alessandri 2006 {published data only}
-
- Alessandri F, Lijoi D, Mistrangelo E, Ferrero S, Ragni N. Randomized study of laparoscopic versus minilaparotomic myomectomy for uterine myomas. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 2006;13(2):92‐7. - PubMed
Alessandri 2010 {published data only}
-
- Alessandri F, Remorgida V, Venturini PL, Ferrero S. Unidirectional barbed suture versus continuous suture with intracorporeal knots in laparoscopic myomectomy: a randomized study. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 2010;17(6):725‐9. - PubMed
Al‐Shabibi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Shabibi N, Korkontzelos I, Gkioulekas N, Stamatopoulos C, Tsibanakos I, Magos A. Cable ties as tourniquets at open myomectomy. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2010;110(3):265‐6. - PubMed
Chang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chang WC, Huang SC, Sheu BC, Shih JC, Hsu WC, Chen SY, Chang DY. Changes in uterine blood flow following laparoscopic myomectomy with or without uterine artery ligation on two‐ and three‐dimensional power Doppler ultrasound. Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2009;33(2):221‐7. - PubMed
Chang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chang WC, Chou LY, Chang DY, Huang PS, Huang SC, Chen SY, Sheu BC. Simultaneous laparoscopic uterine artery ligation and laparoscopic myomectomy for symptomatic uterine myomas with and without in situ morcellation. Human Reproduction 2011;26(7):1735‐40. - PubMed
Chang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chang WC, Huang PS, Wang PH, Chang DY, Huang SC, Chen SY, et al. Comparison of laparoscopic myomectomy using in situ morcellation with and without uterine artery ligation for treatment of symptomatic myomas. Journal of Minimally Invasive Surgery 2012;19(6):715‐21. - PubMed
Fletcher 1996 {published data only}
-
- Fletcher H, Frederick J, Hardie M, Simeon D. A randomized comparison of vasopressin and tourniquet as hemostatic agents during myomectomy. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;87:1014‐8. - PubMed
Frederick 2013 {published data only}
-
- Frederick S, Frederick J, Fletcher H, Reid M, Hardie M, Gardner W. A trial comparing the use of rectal misoprostol plus perivascular vasopressin with perivascular vasopressin alone to decrease myometrial bleeding at the time of abdominal myomectomy. Fertility and Sterility 2013;100(4):1044‐9. - PubMed
Ginsburg 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ginsburg ES, Benson CB, Garfield JM, Gleason RE, Friedman AJ. The effect of operative technique and uterine size on blood loss during myomectomy: a prospective randomized study. Fertility and Sterility 1993;60:956‐62. - PubMed
Kathiresan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kathiresan AS, Brookfield KF, Gonzalez‐quintero VH, Verma U. Vasopressin versus a combination of vasopressin and tourniquets: a comparison of blood loss in patients undergoing abdominal myomectomies. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2011;51(1):79‐83. - PubMed
Kimura 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kimura T, Kusui, Matsumura Y, Ogita K, Isaka S, Nakajima A, et al. Effectiveness of hormonal tourniquet by vasopressin during myomectomy through vasopressin V1a receptor ubiquitously expressed in the myometrium. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 2002;54:125‐31. - PubMed
Lee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lee KH, Park LH. Rapid and secure laparoscopic myomectomy: laparoscopic myomectomy with morcellation and suture by ultraminilaparotomy – a prospective study. Molecular Human Reproduction: 25th Annual Meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology, ESHRE Amsterdam Netherlands. Oxford: Oxford University Press, June 2009:i235.
Lin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lin XN, Zhang SY, Fang SH, Wang MZ, Lou HY. Assessment of different homeostatic methods used in laparoscopic intramural myomectomy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2008;88(13):905‐8. - PubMed
Liu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Liu W, Tang W, Wang I, Tzeng C. Combined laparoscopic uterine artery occlusion and mini‐laparotomy in treating recurrent uterine myomas. 34th Global Congress on Minimally Invasive Gynecology. Chicago, USA, 9‐12 November 2005.
-
- Liu W, Tzeng C, Yi‐Jen C, Wang P. Combining the uterine depletion procedure and myomectomy may be useful for treating symptomatic fibroids. Fertility and Sterility 2004;82:205‐10. - PubMed
Morita 2004 {published data only}
Mousa 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mousa SA, Yassen AM, Alhadary HS, Sadek EES, Abdel‐Hady E‐S. Hematological profile and transfusion requirement during hysteroscopic myomectomy: A comparative study between oxytocin and tranexamic acid infusion. Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia 2012;28(2):125‐32.
Narin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Narin MA, Caliskan E, Kayikcioglu F, Haberal A, Meydanli MM. Blood loss and power Doppler ultrasound characteristics of uterine artery blood flow after 2 levels of bilateral internal iliac artery ligation before extensive myomectomies. The Journal of Reproductive Medicine 2007;52(8):696‐702. - PubMed
Ngeh 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ngeh N, Belli A, Morgan R, Manyonda I. Pre‐myomectomy uterine embolization minimizes operative blood loss. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2004;111:1139‐40. - PubMed
Rossetti 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rossetti A, Paccosi M, Sizzi O, Zulli S, Mancuso S, Lanzone A. Dilute ornitin vasopressin and a myoma drill for laparoscopic myomectomy. The Journal of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists 1999;6:189‐93. - PubMed
Sapmaz 2003B {published data only}
-
- Sapmaz E, Celik H, Altungil A. Bilateral ascending uterine artery ligation vs tourniquet use for hemostasis in cesarian myomectomy. A comparison. The Journal of Reproductive Medicine 2003;48:950‐4. - PubMed
Sapmaz 2003C {published data only}
-
- Sapmaz E, Celik H. Comparison of the effects of the ligation of ascending branches of bilateral arteria uteria with tourniquet method on the intra‐operative and post‐operative hemorrhage in abdominal myomectomy cases. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology 2003;111:74‐7. - PubMed
Wang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wang JJ, Yang F, Gao T, Li L, Xia H, Li HF. Gasless laparoscopy versus conventional laparoscopy in uterine myomectomy: a single‐centre randomized trial. The Journal of International Medical Research 2011;39:172‐8. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Atashkhoei 2012 {unpublished data only}
-
- Atashkhoei S. Effect of oxytocin infusion on reducing operative blood loss during abdominal myomectomy. WHO International Trials Registry Platform 2012. - PubMed
Behdad 2013 {unpublished data only}
-
- Behdad S. The effect of infusion of vitamin C during myomectomy on the blood loss during the procedure and postoperative pain. WHO International Trials Registry Platform 2013.
Additional references
Aubuchon 2002
-
- Aubuchon M, Pinto AB, Williams DB. Treatment of uterine fibroids. Primary Care Update for Ob/Gyns 2002;9:231‐7.
Baldoni 1995
-
- Baldoni A, Moscioni P, Colonnelli M, Affronti G, Garardi G. The possibility of using sulprostone during laparoscopic myomectomy in uterine fibromyomatosis. Preminary studies. Minerva Ginecologica 1995;47:341‐6. - PubMed
Burkert 1983
-
- Burkert H. Clinical overview of mesna. Cancer Treatment Review 1983;10 Suppl A:175‐87. - PubMed
Cooper 2000
-
- Cooper JM, Brady RM. Intraoperative and early postoperative complications of operative hysteroscopy. Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America 2000;27:347‐66. - PubMed
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Practical aspects in monitoring: a brief review. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6:753‐60. - PubMed
Denaro 2001
-
- Denaro V, Forriol F, Martino A, Denaro L, Papalia R, Caione G. Effect of a mucolytic agent on collagen fibres. An optical and polarized light histology study. European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology 2001;11:209‐12.
Derman 1991
-
- Derman G, Rehnstrm J, Neuwirth S. The long‐term effectiveness of hysteroscopic treatment of menorrhagia and leiomyomas. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1991;77:591‐4. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177‐88. - PubMed
Dimitrov 1999
-
- Dimitrov A. The use of the vasoconstrictor hemostatic Remestyp in surgical obstetrics. Akusherstvo i Ginekologiia (Sofia) 1999;38:58‐60. - PubMed
Dubuisson 1997
-
- Dubuisson JB, Chapron C, Fauconnier A, Kreiker G. Laparoscopic myomectomy and myolysys. Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology 1997;9:233‐8. - PubMed
Dunn 1999
-
- Dunn CJ, Goa KL. Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in surgery and other indications. Drugs 1999;57(6):1005‐32. - PubMed
Farquhar 2002
-
- Farquhar CM, Brown PM, Furness S. Cost‐effectiveness of preoperative gonadotrophin releasing analogues for women with uterine fibroids undergoing hysterectomy or myomectomy. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2002;109:1273‐80. - PubMed
Fedele 1995
-
- Fedele L, Parazzini F, Luchini L, Mezzopane R, Tozzi L, Villa L. Recurrence of fibroids after myomectomy: a transvaginal ultrasonographic study. Human Reproduction 1995;10:1795‐6. - PubMed
Frederick 2002
-
- Frederick J, Hardie M, Reid M, Fletcher H, Wynter S, Frederick C. Operative morbidity and reproductive outcomes in secondary myomectomy: a prospective cohort. Human Reproduction 2002;17:2967‐71. - PubMed
Fuchs 1984
-
- Fuchs AR, Fuchs F, Husslein P, Soloff MS. Oxytocin receptors in the human uterus during pregnancy and parturition. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1984;150:734‐41. - PubMed
Garnet 1964
-
- Garnet JD. Uterine rupture during pregnancy. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1964;23:898‐905. - PubMed
Hasson 1992
-
- Hasson HM, Rotman C, Rana N. Laparoscopic myomectomy. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1992;80:884‐8. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. http://www.cochrane.org/training/cochrane‐handbook/ (accessed 30th March 2011).
Holub 2003
-
- Hulob Z, Lukac J, Kliment L, Urbanet S. Short‐term results from laparoscopic dissection of uterine vessels in women with symptomatic fibroids. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology 2003;110(1):94‐8. - PubMed
Hurst 2005
-
- Hurst BS, Mathews ML, Marshburn PB. Laparoscopic myomectomy for symptomatic uterine myomas. Fertility and Sterility 2005;83(1):1‐23. - PubMed
Hutchins 1996
-
- Hutchins FL Jr. A randomized comparison of vasopressin and tourniquet as hemostatic agents during myomectomy. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;88:639‐40. - PubMed
Iverson 1996
-
- Iverson RE Jr, Chelmow D, Strohbehn K, Waldman L, Evanstash EG. Relative morbidity of abdominal hysterectomy and myomectomy for the management of uterine leiomyomas. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;88:415‐9. - PubMed
Iverson 1999
-
- Iverson RE Jr, Chelmow D, Strohbehn K. Myomectomy fever: testing the dogma. Fertility and Sterility 1999;72:104‐8. - PubMed
Jacoby 2010
Koh 2003
-
- Koh MBC, Hunt BJ. The management of perioperative bleeding. Blood Reviews 2003;17:179‐85. - PubMed
LaMote 1993
-
- LaMote AI, Lalwani S, Diamond MP. Morbidity associated with abdominal myomectomy. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1993;82:897‐900. - PubMed
Lethaby 2001
Liu 2001
-
- Liu WM, Ng HT, Wu YC, Yen YK, Yuan CC. Laparoscopic bipolar coagulation of uterine vessels: a new method for treating symptomatic fibroids. Fertility and Sterility 2001;75:417‐22. - PubMed
Lumsden 2002
-
- Lumsden MA. Embolization versus myomectomy versus hysterectomy: which is best, when?. Human Reproduction 2002;17:253‐9. - PubMed
McLaughin 1985
-
- McLaughin DS. Metroplasty and myomectomy with CO2 laser for maximizing the preservation of normal tissue and minimizing blood loss. The Journal of Reproductive Medicine 1985;30:1‐9. - PubMed
Nishiyama 2006
-
- Nishiyama S, Saito M, Sato K, Kurishito M, Itasaka T, Shioda K. High recurrence rate of uterine fibroids on transvaginal ultrasound after abdominal myomectomy in Japanese women. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 2006;61:155‐9. - PubMed
Ravina 1995
-
- Ravina JH, Herbreteau D, Ciraru‐Vigneron N, et al. Arterial embolisation to treat uterine myomata. Lancet 1995;346:671‐72. - PubMed
Somigliana 2008
-
- Somigliana E, Vercellini P, Benaglia L, Abbiati A, Barbara G, Fedele L. The role of myomectomy in fertility enhancement. Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology 2008;20(4):379‐85. - PubMed
Tulandi 1993
-
- Tulandi T, Murray C, Gualnick M. Adhesion formation and reproductive outcome after myomectomy and second‐look laparoscopy. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1993;82:213‐5. - PubMed
Vercellini 1993
-
- Vercellini P, Vendola N, Ragni G, Trespidi L, Oldani S, Crosignani PG. Abnormal uterine bleeding associated with iron‐deficiency anaemia: Etiology and role of hysteroscopy. The Journal of Reproductive Medicine 1993;38:502‐4. - PubMed
Vollenhoven 1990
-
- Vollenhoven BJ, Lawrence AS, Healey DL. Uterine fibroids. A clinical review. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1990;97:285‐98. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Kongnyuy 2007
Kongnyuy 2008
-
- Kongnyuy EJ, Broek N, Wiysonge CS. A systematic review of randomised controlled trials to reduce hemorrhage during myomectomy for uterine fibroids. International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics 2008;100(1):4‐9. - PubMed
Kongnyuy 2009
Kongnyuy 2011
-
- Kongnyuy EJ, Wiysonge CS. Interventions to reduce haemorrhage during myomectomy for fibroids. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 11. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005355.pub4] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

