Neuroanatomical precursors of dyslexia identified from pre-reading through to age 11
- PMID: 25125610
- PMCID: PMC4240283
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awu229
Neuroanatomical precursors of dyslexia identified from pre-reading through to age 11
Abstract
Developmental dyslexia is a common reading disorder that negatively impacts an individual's ability to achieve literacy. Although the brain network involved in reading and its dysfunction in dyslexia has been well studied, it is unknown whether dyslexia is caused by structural abnormalities in the reading network itself or in the lower-level networks that provide input to the reading network. In this study, we acquired structural magnetic resonance imaging scans longitudinally from 27 Norwegian children from before formal literacy training began until after dyslexia was diagnosed. Thus, we were able to determine that the primary neuroanatomical abnormalities that precede dyslexia are not in the reading network itself, but rather in lower-level areas responsible for auditory and visual processing and core executive functions. Abnormalities in the reading network itself were only observed at age 11, after children had learned how to read. The findings suggest that abnormalities in the reading network are the consequence of having different reading experiences, rather than dyslexia per se, whereas the neuroanatomical precursors are predominantly in primary sensory cortices.
Keywords: cortical thickness; development; neuroimaging; paediatric; reading.
© The Author (2014). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
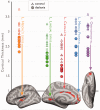
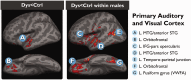

Comment in
-
The neural basis of dyslexia may originate in primary auditory cortex.Brain. 2014 Dec;137(Pt 12):3100-2. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu296. Brain. 2014. PMID: 25413932 No abstract available.
-
Reply: Cortical differences in preliterate children at familiar risk of dyslexia are similar to those observed in dyslexic readers.Brain. 2015 Sep;138(Pt 9):e379. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv037. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25701064 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cortical differences in preliterate children at familiar risk of dyslexia are similar to those observed in dyslexic readers.Brain. 2015 Sep;138(Pt 9):e378. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv036. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25701065 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Tackling the 'dyslexia paradox': reading brain and behavior for early markers of developmental dyslexia.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2016 Mar-Apr;7(2):156-76. doi: 10.1002/wcs.1383. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2016. PMID: 26836227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical gray matter in children with dyslexia before the onset of reading instruction.Cortex. 2019 Dec;121:399-413. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2019.09.010. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Cortex. 2019. PMID: 31704534
-
Decreased functional connectivity in the fronto-parietal network in children with mood disorders compared to children with dyslexia during rest: An fMRI study.Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Mar 1;18:582-590. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.02.034. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 29845006 Free PMC article.
-
Voxel and surface based whole brain analysis shows reading skill associated grey matter abnormalities in dyslexia.Sci Rep. 2021 May 25;11(1):10862. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89317-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34035329 Free PMC article.
-
The visual deficit theory of developmental dyslexia.Neuroimage. 1996 Dec;4(3 Pt 3):S108-17. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1996.0061. Neuroimage. 1996. PMID: 9345535 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurobiological Sex Differences in Developmental Dyslexia.Front Psychol. 2019 Jan 11;9:2669. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02669. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30687153 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of comorbidity burden and age on brain integrity in HIV.AIDS. 2019 Jun 1;33(7):1175-1185. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002192. AIDS. 2019. PMID: 30870195 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroanatomical anomalies of dyslexia: Disambiguating the effects of disorder, performance, and maturation.Neuropsychologia. 2016 Jan 29;81:68-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.12.003. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Neuropsychologia. 2016. PMID: 26679527 Free PMC article.
-
Intergenerational transmission of the structure of the auditory cortex and reading skills.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 11:2024.09.11.610780. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.610780. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39314393 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Neural encoding of the speech envelope by children with developmental dyslexia.Brain Lang. 2016 Sep;160:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2016.06.006. Epub 2016 Jul 17. Brain Lang. 2016. PMID: 27433986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berninger VW, Raskind W, Richards T, Abbott R, Stock P. A multidisciplinary approach to understanding developmental dyslexia within working-memory architecture: genotypes, phenotypes, brain, and instruction. Dev Neuropsychol. 2008;33:707–44. - PubMed
-
- Carlsten CT. Leseprøve 6. klasse bokmål og nynorsk [Reading test 6th grade bokmål and nynorsk] Oslo: Damm & Søn AS; 2002.
-
- Clarke S, Miklossy J. Occipital cortex in man: organization of callosal connections, related myelo- and cytoarchitecture, and putative boundaries of functional visual areas. J Comp Neurol. 1990;298:188–214. - PubMed
-
- Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI. Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage. 1999;9:179–94. - PubMed
-
- Eckert MA, Leonard CM, Richards TL, Aylward EH, Thomson J, Berninger VW. Anatomical correlates of dyslexia: frontal and cerebellar findings. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 2):482–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

