Single-stage management of large pulmonary and hepatic hydatid cysts in pediatric age group: Report of two cases
- PMID: 25125816
- PMCID: PMC4129601
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-2113.135773
Single-stage management of large pulmonary and hepatic hydatid cysts in pediatric age group: Report of two cases
Abstract
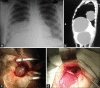
Two patients presented to us with very similar clinical and radiological presentation of huge hydatid cysts in the lung and liver. The first patient was an 11-year-old female child and the second one was a 9-year-old male child. The clinical features in both were breathlessness on exertion, pain abdomen, and abdominal distension. Chest Roentgenogram along with computed tomogram of the chest and abdomen revealed presence of thin-walled homogenous large cysts, one in the right lung and two in the liver, in both the cases. Although the liver cysts were of larger size and occupying most of the right lobe of the liver and part of the left lobe, liver function tests were normal. All three cysts were enucleated in the same sitting by a combined thoracic and abdominal approach (thoracotomy followed by laparotomy). After enucleation of the cyst, capitonnage of the cavity in the lung was done and the liver cavities were filled with omentum to prevent collection of fluid and abscess formation. Both patients recovered well, although the second patient required abdominal drain for a long period of 1 month for bile leakage which decreased gradually and eventually stopped.
Keywords: Huge hydatid cysts; laparotomy; single-stage management; thoracotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concomitant Lung and Liver Hydatid Cyst Managed as One-Stage Surgery.Maedica (Bucur). 2017 Jan;12(1):19-22. Maedica (Bucur). 2017. PMID: 28878832 Free PMC article.
-
Management of a patient with hepatic-thoracic-pelvic and omental hydatid cysts and post-operative bilio-cutaneous fistula: a case report.Hepatogastroenterology. 1999 Jul-Aug;46(28):2202-7. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. PMID: 10521968
-
Single-stage transthoracic approach for right lung and liver hydatid disease.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003 Sep;126(3):769-73. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5223(03)00366-0. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003. PMID: 14502152
-
Thoracic amebiasis.Clin Chest Med. 2002 Jun;23(2):479-92. doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(01)00008-9. Clin Chest Med. 2002. PMID: 12092041 Review.
-
Parenchyma-preserving surgery in the management of pulmonary hydatid cysts.J Invest Surg. 2006 Jan-Feb;19(1):61-8. doi: 10.1080/08941930500444586. J Invest Surg. 2006. PMID: 16546931 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Growth of Hydatid Cyst: A Pediatric Case Report.Iran J Parasitol. 2021 Jan-Mar;16(1):164-167. doi: 10.18502/ijpa.v16i1.5538. Iran J Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33786059 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant Lung and Liver Hydatid Cyst Managed as One-Stage Surgery.Maedica (Bucur). 2017 Jan;12(1):19-22. Maedica (Bucur). 2017. PMID: 28878832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Djuricic SM, Grebeldinger S, Kafka DI, Djan I, Vukadin M, Vasiljevic ZV. Cystic echinococcosis in children - the seventeen-year experience of two large medical centers in Serbia. Parasitol Int. 2010;59:257–61. - PubMed
-
- Minaev SV, Gerasimenko IN, Bykov NI, Timofeev SV. Up-to-date approaches in treatment of hydatid disease of the liver in childhood. Vestn Khir Im I I Grek. 2013;172:71–4. - PubMed
-
- Iyigun O, Uysal S, Sancak R, Hokelek M, Uyar Y, Bernay F, et al. Multiple organ involvement hydatid cysts in a 2-year-old boy. J Trop Pediatr. 2004;50:374–6. - PubMed
-
- Slim MS, Akel SR. Hydatidosis in childhood. Prog Pediatr Surg. 1982;15:119–29. - PubMed
-
- Dopchiz MC, Elissondo MC, Andresiuk MV, Maiorini E, Gutiérrez AM, Muzulin PM, et al. Pediatric hydatidosis in the south-east of the Buenos Aires province, Argentina. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2009;41:105–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

