Stem-loop recognition by DDX17 facilitates miRNA processing and antiviral defense
- PMID: 25126784
- PMCID: PMC4134512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.023
Stem-loop recognition by DDX17 facilitates miRNA processing and antiviral defense
Abstract
DEAD-box helicases play essential roles in RNA metabolism across species, but emerging data suggest that they have additional functions in immunity. Through RNAi screening, we identify an evolutionarily conserved and interferon-independent role for the DEAD-box helicase DDX17 in restricting Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV), a mosquito-transmitted virus in the bunyavirus family that causes severe morbidity and mortality in humans and livestock. Loss of Drosophila DDX17 (Rm62) in cells and flies enhanced RVFV infection. Similarly, depletion of DDX17 but not the related helicase DDX5 increased RVFV replication in human cells. Using crosslinking immunoprecipitation high-throughput sequencing (CLIP-seq), we show that DDX17 binds the stem loops of host pri-miRNA to facilitate their processing and also an essential stem loop in bunyaviral RNA to restrict infection. Thus, DDX17 has dual roles in the recognition of stem loops: in the nucleus for endogenous microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis and in the cytoplasm for surveillance against structured non-self-elements.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
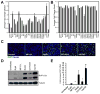
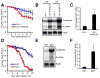
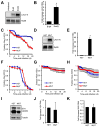
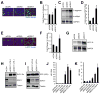
Comment in
-
DDX17: structured RNA recognition drives diverse outputs.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(22):3467-8. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.980695. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25493410 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Boutros M, Kiger AA, Armknecht S, Kerr K, Hild M, Koch B, Haas SA, Paro R, Perrimon N. Genome-wide RNAi analysis of growth and viability in Drosophila cells. Science. 2004;303:832–835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI095500/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI074951/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095500/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057168/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074951/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007324/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI074951/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54AI057168/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067719/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM103383/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM103383/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32AI007324/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

