CellNet: network biology applied to stem cell engineering
- PMID: 25126793
- PMCID: PMC4233680
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.020
CellNet: network biology applied to stem cell engineering
Abstract
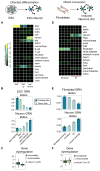
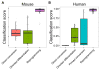
Somatic cell reprogramming, directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells, and direct conversions between differentiated cell lineages represent powerful approaches to engineer cells for research and regenerative medicine. We have developed CellNet, a network biology platform that more accurately assesses the fidelity of cellular engineering than existing methodologies and generates hypotheses for improving cell derivations. Analyzing expression data from 56 published reports, we found that cells derived via directed differentiation more closely resemble their in vivo counterparts than products of direct conversion, as reflected by the establishment of target cell-type gene regulatory networks (GRNs). Furthermore, we discovered that directly converted cells fail to adequately silence expression programs of the starting population and that the establishment of unintended GRNs is common to virtually every cellular engineering paradigm. CellNet provides a platform for quantifying how closely engineered cell populations resemble their target cell type and a rational strategy to guide enhanced cellular engineering.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
CellNet--where your cells are standing.Cell. 2014 Aug 14;158(4):699-701. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.001. Cell. 2014. PMID: 25126778
-
A systems view of cellular reprogramming.Nat Methods. 2014 Oct;11(10):987. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3126. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 25392878 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, Garreta E, Consiglio A, Gonzalez F, Vassena R, Bilic J, Pekarik V, Tiscornia G, et al. Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:1276–1284. - PubMed
-
- Breiman L. Random Forests. Machine Learning. 2001;45:5–32.
-
- Caiazzo M, Dell’Anno MT, Dvoretskova E, Lazarevic D, Taverna S, Leo D, Sotnikova TD, Menegon A, Roncaglia P, Colciago G, et al. Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nature. 2011;476:224–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 HG005550/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL066987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK096013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50HG005550/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL066987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK096013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24DK092760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL100001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R24 DK092760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL007623/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007623/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

