D-beta-hydroxybutyrate extends lifespan in C. elegans
- PMID: 25127866
- PMCID: PMC4169858
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100683
D-beta-hydroxybutyrate extends lifespan in C. elegans
Abstract
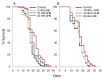
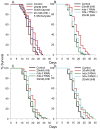
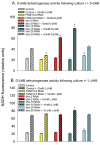
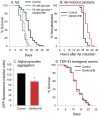
The ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate (βHB) is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor and has been shown to be protective in many disease models, but its effects on aging are not well studied. Therefore we determined the effect of βHB supplementation on the lifespan ofC. elegans nematodes. βHB supplementation extended mean lifespan by approximately 20%. RNAi knockdown of HDACs hda-2 or hda-3 also increased lifespan and further prevented βHB-mediated lifespan extension. βHB-mediated lifespan extension required the DAF-16/FOXO and SKN-1/Nrf longevity pathways, the sirtuin SIR-2.1, and the AMP kinase subunit AAK-2. βHB did not extend lifespan in a genetic model of dietary restriction indicating that βHB is likely functioning through a similar mechanism. βHB addition also upregulated ΒHB dehydrogenase activity and increased oxygen consumption in the worms. RNAi knockdown of F55E10.6, a short chain dehydrogenase and SKN-1 target gene, prevented the increased lifespan and βHB dehydrogenase activity induced by βHB addition, suggesting that F55E10.6 functions as an inducible βHB dehydrogenase. Furthermore, βHB supplementation increased worm thermotolerance and partially prevented glucose toxicity. It also delayed Alzheimer's amyloid-beta toxicity and decreased Parkinson's alpha-synuclein aggregation. The results indicate that D-βHB extends lifespan through inhibiting HDACs and through the activation of conserved stress response pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest could be disclosed for any author.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of amino acid-mediated lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans.BMC Genet. 2015 Feb 3;16(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12863-015-0167-2. BMC Genet. 2015. PMID: 25643626 Free PMC article.
-
Hibiscus sabdariffa L. extract prolongs lifespan and protects against amyloid-β toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans: involvement of the FoxO and Nrf2 orthologues DAF-16 and SKN-1.Eur J Nutr. 2020 Feb;59(1):137-150. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-01894-w. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Eur J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30710163
-
Malate and fumarate extend lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058345. Epub 2013 Mar 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23472183 Free PMC article.
-
d-Allulose, a stereoisomer of d-fructose, extends Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan through a dietary restriction mechanism: A new candidate dietary restriction mimetic.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Dec 2;493(4):1528-1533. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.147. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28965946
-
Ketone bodies mimic the life span extending properties of caloric restriction.IUBMB Life. 2017 May;69(5):305-314. doi: 10.1002/iub.1627. Epub 2017 Apr 3. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28371201 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Understanding of the Role of Lipid Metabolism in Aging.Cells. 2021 Apr 13;10(4):880. doi: 10.3390/cells10040880. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33924316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate ameliorates neurodevelopmental deficits in the GABAergic system of daf-18/PTEN Caenorhabditis elegans mutants.Elife. 2024 Oct 18;13:RP94520. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94520. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39422188 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune cell-intrinsic ketogenesis is dispensable for organismal metabolism and age-related inflammation.J Biol Chem. 2023 Mar;299(3):103005. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.103005. Epub 2023 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36775129 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the gut microbiome during host ageing.F1000Res. 2018 Jul 16;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1086. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.15121.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 30057748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to Slow down the Ticking Clock: Age-Associated Epigenetic Alterations and Related Interventions to Extend Life Span.Cells. 2022 Jan 29;11(3):468. doi: 10.3390/cells11030468. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahlqvist KJ, Hamalainen RH, Yatsuga S, Uutela M, Terzioglu M, Gotz A, Forsstrom S, Salven P, Angers-Loustau A, Kopra OH, Tyynismaa H, Larsson NG, Wartiovaara K, et al. Somatic progenitor cell vulnerability to mitochondrial DNA mutagenesis underlies progeroid phenotypes in Polg mutator mice. Cell Metab. 2012;15:100–109. - PubMed
-
- Trifunovic A, Wredenberg A, Falkenberg M, Spelbrink JN, Rovio AT, Bruder CE, Bohlooly YM, Gidlof S, Oldfors A, Wibom R, Tornell J, Jacobs HT, Larsson NG. Premature ageing in mice expressing defective mitochondrial DNA polymerase. Nature. 2004;429:417–423. - PubMed
-
- Braeckman BP, Houthoofd K, De Vreese A, Vanfleteren JR. Apparent uncoupling of energy production and consumption in long-lived Clk mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr Biol. 1999;9:493–496. - PubMed
-
- Dell'agnello C, Leo S, Agostino A, Szabadkai G, Tiveron C, Zulian A, Prelle A, Roubertoux P, Rizzuto R, Zeviani M. Increased longevity and refractoriness to Ca(2+)-dependent neurodegeneration in Surf1 knockout mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:431–444. - PubMed
-
- Copeland JM, Cho J, Lo T, Jr, Hur JH, Bahadorani S, Arabyan T, Rabie, J, Soh J, Walker DW. Extension of Drosophila life span by RNAi of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Curr Biol. 2009;19:1591–1598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

