Citrate anticoagulation versus systemic heparinisation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a multi-center randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 25128022
- PMCID: PMC4161888
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-014-0472-6
Citrate anticoagulation versus systemic heparinisation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a multi-center randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: Because of ongoing controversy, renal and vital outcomes are compared between systemically administered unfractionated heparin and regional anticoagulation with citrate-buffered replacement solution in predilution mode, during continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH) in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury (AKI).
Methods: In this multi-center randomized controlled trial, patients admitted to the intensive care unit requiring CVVH and meeting inclusion criteria, were randomly assigned to citrate or heparin. Primary endpoints were mortality and renal outcome in intention-to-treat analysis. Secondary endpoints were safety and efficacy. Safety was defined as absence of any adverse event necessitating discontinuation of the assigned anticoagulant. For efficacy, among other parameters, survival times of the first hemofilter were studied.
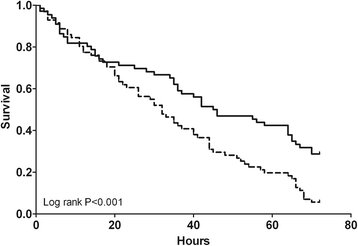
Results: Of the 139 patients enrolled, 66 were randomized to citrate and 73 to heparin. Mortality rates at 28 and 90 days did not differ between groups: 22/66 (33%) of citrate-treated patients died versus 25/72 (35%) of heparin-treated patients at 28 days, and 27/65 (42%) of citrate-treated patients died versus 29/69 (42%) of heparin-treated patients at 90 days (P = 1.00 for both). Renal outcome, i.e. independency of renal replacement therapy 28 days after initiation of CVVH in surviving patients, did not differ between groups: 29/43 (67%) in the citrate-treated patients versus 33/47 (70%) in heparin-treated patients (P = 0.82). Heparin was discontinued in 24/73 (33%) of patients whereas citrate was discontinued in 5/66 (8%) of patients (P < 0.001). Filter survival times were superior for citrate (median 46 versus 32 hours, P = 0.02), as were the number of filters used (P = 0.002) and the off time within 72 hours (P = 0.002). The costs during the first 72 hours of prescribed CVVH were lower in citrate-based CVVH.
Conclusions: Renal outcome and patient mortality were similar for citrate and heparin anticoagulation during CVVH in the critically ill patient with AKI. However, citrate was superior in terms of safety, efficacy and costs.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT00209378. Registered 13th September 2005.
Figures

Comment in
-
Citrate for continuous renal replacement therapy: safer, better and cheaper.Crit Care. 2014 Dec 3;18(6):661. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0661-3. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 25673124 Free PMC article.
-
Some metabolic issues should not be neglected when using citrate for continuous renal replacement therapy!Crit Care. 2015 Feb 6;19(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0766-3. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25738824 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C. Beginning and ending supportive therapy for the kidney (BEST Kidney) investigators, acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.7.813. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mehta RL, McDonald BR, Ward DM. Regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous arteriovenous hemodialysis. Contrib Nephrol. 1991;93:210–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

