QTug.sau-3B is a major quantitative trait locus for wheat hexaploidization
- PMID: 25128436
- PMCID: PMC4199700
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.114.013078
QTug.sau-3B is a major quantitative trait locus for wheat hexaploidization
Abstract
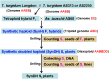
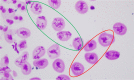
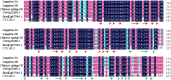
Meiotic nonreduction resulting in unreduced gametes is thought to be the predominant mechanism underlying allopolyploid formation in plants. Until now, however, its genetic base was largely unknown. The allohexaploid crop common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), which originated from hybrids of T. turgidum L. with Aegilops tauschii Cosson, provides a model to address this issue. Our observations of meiosis in pollen mother cells from T. turgidum×Ae. tauschii hybrids indicated that first division restitution, which exhibited prolonged cell division during meiosis I, was responsible for unreduced gamete formation. A major quantitative trait locus (QTL) for this trait, named QTug.sau-3B, was detected on chromosome 3B in two T. turgidum×Ae. tauschii haploid populations. This QTL is situated between markers Xgwm285 and Xcfp1012 and covered a genetic distance of 1 cM in one population. QTug.sau-3B is a haploid-dependent QTL because it was not detected in doubled haploid populations. Comparative genome analysis indicated that this QTL was close to Ttam-3B, a collinear homolog of tam in wheat. Although the relationship between QTug.sau-3B and Ttam requires further study, high frequencies of unreduced gametes may be related to reduced expression of Ttam in wheat.
Keywords: CYCA1;2/TAM; Triticum aestivum; allopolyploidy; first division restitution; unreduced gametes.
Copyright © 2014 Hao et al.
Figures



References
-
- Bretagnolle F., Thompson J. D., 1995. Gametes with the stomatic chromosome number: mechanisms of their formation and role in the evolution of autopolypoid plants. New Phytol. 129: 1–22 - PubMed
-
- Brownfield L., Köhler C., 2011. Unreduced gamete formation in plants: mechanisms and prospects. J. Exp. Bot. 62: 1659–1668 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
