Role of hypoxia-induced transglutaminase 2 in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation
- PMID: 25128524
- PMCID: PMC4187037
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00162.2014
Role of hypoxia-induced transglutaminase 2 in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation
Abstract
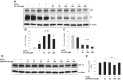
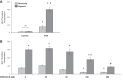
We previously reported that transglutaminase 2 (TG2) activity is markedly elevated in lungs of hypoxia-exposed rodent models of pulmonary hypertension (PH). Since vascular remodeling of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) is important in PH, we undertook the present study to determine whether TG2 activity is altered in PASMCs with exposure to hypoxia and whether that alteration participates in their proliferative response to hypoxia. Cultured distal bovine (b) and proximal human (h) PASMCs were exposed to hypoxia (3% O2) or normoxia (21% O2). mRNA and protein expression were determined by PCR and Western blot analyses. TG2 activity and function were visualized and determined by fluorescent labeled 5-pentylamine biotin incorporation and immunoblotting of serotonylated fibronectin. Cell proliferation was assessed by [(3)H]thymidine incorporation assay. At 24 h, both TG2 expression and activity were stimulated by hypoxia in bPASMCs. Activation of TG2 by hypoxia was blocked by inhibition of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor or the transient receptor potential channel V4. In contrast, TG2 expression was blocked by inhibition of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, supporting the presence of separate mechanisms for stimulation of activity and expression of TG2. Pulmonary arterial hypertension patient-derived hPASMCs were found to proliferate significantly more rapidly and respond to hypoxia more strongly than control-derived hPASMCs. Similar to bovine cells, hypoxia-induced proliferation of patient-derived cells was blocked by inhibition of TG2 activity. Our results suggest an important role for TG2, mediated by intracellular calcium fluxes and HIF-1α, in hypoxia-induced PASMC proliferation and possibly in vascular remodeling in PH.
Keywords: CaSR; HIF-1α; TG2; TRPV4; pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dynamin-related protein 1-mediated mitochondrial mitotic fission permits hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and offers a novel therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension.Circ Res. 2012 May 25;110(11):1484-97. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.263848. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22511751 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue transglutaminase promotes serotonin-induced AKT signaling and mitogenesis in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells.Cell Signal. 2014 Dec;26(12):2818-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25218191 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 promotes hypoxic pulmonary hypertension through stabilization of DPP4 in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Oct 1;442(2):114254. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114254. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39276964
-
Transglutaminase 2-mediated serotonylation in pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Feb 15;306(4):L309-15. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00321.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24375797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium sensing receptor: A promising therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension.Life Sci. 2024 Mar 1;340:122472. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122472. Epub 2024 Jan 28. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38290572 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation, Autoimmunity, and Hypertension: The Essential Role of Tissue Transglutaminase.Am J Hypertens. 2017 Aug 1;30(8):756-764. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpx027. Am J Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28338973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonylation: Serotonin Signaling and Epigenetics.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov 21;12:288. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00288. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31824263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting transglutaminase 2 mediated exostosin glycosyltransferase 1 signaling in liver cancer stem cells with acyclic retinoid.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jun 13;14(6):358. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05847-4. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37308486 Free PMC article.
-
How cells channel their stress: Interplay between Piezo1 and the cytoskeleton.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Nov;71:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.06.018. Epub 2017 Jul 1. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28676421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenethylaminylation: Preliminary In Vitro Evidence for the Covalent Transamidation of Psychedelic Phenethylamines to Glial Proteins using 3,5-Dimethoxy-4-(2-Propynyloxy)-Phenethylamine as a Model Compound.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 17:2025.02.13.638188. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.13.638188. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40027829 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Ball MK, Waypa GB, Mungai PT, Nielsen JM, Czech L, Dudley VJ, Beussink L, Dettman RW, Berkelhamer SK, Steinhorn RH, Shah SJ, Schumacker PT. Regulation of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by vascular smooth muscle hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 189: 314–324, 2014 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonnet S, Michelakis ED, Porter CJ, Andrade-Navarro MA, Thebaud B, Haromy A, Harry G, Moudgil R, McMurtry MS, Weir EK, Archer SL. An abnormal mitochondrial-hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha-Kv channel pathway disrupts oxygen sensing and triggers pulmonary arterial hypertension in fawn hooded rats: similarities to human pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 113: 2630–2641, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

