Multiplexed aberration measurement for deep tissue imaging in vivo
- PMID: 25128976
- PMCID: PMC4180771
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3068
Multiplexed aberration measurement for deep tissue imaging in vivo
Abstract
We describe an adaptive optics method that modulates the intensity or phase of light rays at multiple pupil segments in parallel to determine the sample-induced aberration. Applicable to fluorescent protein-labeled structures of arbitrary complexity, it allowed us to obtain diffraction-limited resolution in various samples in vivo. For the strongly scattering mouse brain, a single aberration correction improved structural and functional imaging of fine neuronal processes over a large imaging volume.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
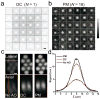
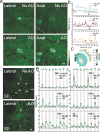
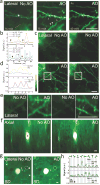
References
-
- Kubby J, editor. Adaptive Optics for Biological Imaging. CRC Press; 2013.
-
- Milkie DE, Betzig E, Ji N. Opt Lett. 2011;36:4206–4208. - PubMed
-
- Ji N, Milkie DE, Betzig E. Nat Methods. 2010;7:141–147. - PubMed
-
- Liu R, Milkie DE, Kerlin A, MacLennan B, Ji N. Opt Express. 2014;22:1619–1628. - PubMed
-
- Bridges WB, et al. Appl Opt. 1974;13:291–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

