Joint analysis of three genome-wide association studies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese populations
- PMID: 25129146
- PMCID: PMC4212832
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3064
Joint analysis of three genome-wide association studies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese populations
Abstract
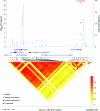
We conducted a joint (pooled) analysis of three genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) in individuals of Chinese ancestry (5,337 ESCC cases and 5,787 controls) with 9,654 ESCC cases and 10,058 controls for follow-up. In a logistic regression model adjusted for age, sex, study and two eigenvectors, two new loci achieved genome-wide significance, marked by rs7447927 at 5q31.2 (per-allele odds ratio (OR) = 0.85, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.82-0.88; P = 7.72 × 10(-20)) and rs1642764 at 17p13.1 (per-allele OR = 0.88, 95% CI = 0.85-0.91; P = 3.10 × 10(-13)). rs7447927 is a synonymous SNP in TMEM173, and rs1642764 is an intronic SNP in ATP1B2, near TP53. Furthermore, a locus in the HLA class II region at 6p21.32 (rs35597309) achieved genome-wide significance in the two populations at highest risk for ESSC (OR = 1.33, 95% CI = 1.22-1.46; P = 1.99 × 10(-10)). Our joint analysis identifies new ESCC susceptibility loci overall as well as a new locus unique to the population in the Taihang Mountain region at high risk of ESCC.
Figures

References
-
- Wang LD, et al. Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:759–763. - PubMed
-
- Wu C, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies three new susceptibility loci for esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in Chinese populations. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:679–684. - PubMed
-
- Wu C, et al. Genome-wide association analyses of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese identify multiple susceptibility loci and gene-environment interactions. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:1090–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R37 CA70837/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA80205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA173640/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA053890/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA055069/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200477001C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182876/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA CP000112/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA144034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP011010/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA82729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA CP000150/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

