2014 AATS guidelines for the prevention and management of perioperative atrial fibrillation and flutter for thoracic surgical procedures
- PMID: 25129609
- PMCID: PMC4454633
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.06.036
2014 AATS guidelines for the prevention and management of perioperative atrial fibrillation and flutter for thoracic surgical procedures
Figures


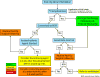


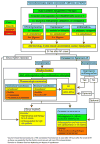

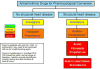

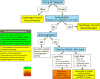
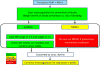
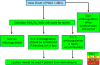
References
-
- Institute of Medicine (U.S.) Clinical practice guidelines we can trust. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011. Committee on Standards for Developing Trustworthy Clinical Practice Guidelines and R. 1. Graham.
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Cleveland JC, Cigarroa JE, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Murray KT, Sacco RL, Stevenson WG, Tchou PJ, Tracy CM, Yancy CW. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation, Apr. 2014 - PubMed
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Cleveland JC, Cigarroa JE, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Murray KT, Sacco RL, Stevenson WG, Tchou PJ, Tracy CM, Yancy CW. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation, Apr. 2014 - PubMed
-
- Fernando HC, Jaklitsch MT, Walsh GL, Tisdale JE, Bridges CD, Mitchell JD, Shrager JB. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons practice guideline on the prophylaxis and management of atrial fibrillation associated with general thoracic surgery: executive summary. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011 Sep;92(3):1144–1152. - PubMed
-
- Vaporciyan AA, Correa AM, Rice DC, Roth JA, Smythe WR, Swisher SG, Walsh GL., Jr Risk factors associated with atrial fibrillation after noncardiac thoracic surgery: analysis of 2588 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004 Mar;127(3):779–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

