Absence of a simple code: how transcription factors read the genome
- PMID: 25129887
- PMCID: PMC4149858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.07.002
Absence of a simple code: how transcription factors read the genome
Abstract
Transcription factors (TFs) influence cell fate by interpreting the regulatory DNA within a genome. TFs recognize DNA in a specific manner; the mechanisms underlying this specificity have been identified for many TFs based on 3D structures of protein-DNA complexes. More recently, structural views have been complemented with data from high-throughput in vitro and in vivo explorations of the DNA-binding preferences of many TFs. Together, these approaches have greatly expanded our understanding of TF-DNA interactions. However, the mechanisms by which TFs select in vivo binding sites and alter gene expression remain unclear. Recent work has highlighted the many variables that influence TF-DNA binding, while demonstrating that a biophysical understanding of these many factors will be central to understanding TF function.
Keywords: DNA binding specificity models; chromatin; cofactor; cooperativity; high-throughput binding assays; protein-DNA recognition.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
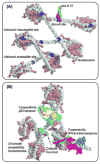
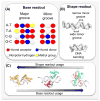

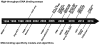
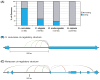

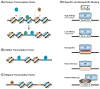
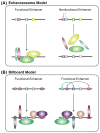

References
-
- Stormo GD. DNA binding sites: representation and discovery. Bioinformatics. 2000;16:16–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

