Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Aortic Intima-Media Thickness in Patients Without Clinical Manifestation of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 25130180
- PMCID: PMC6806715
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21770
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Aortic Intima-Media Thickness in Patients Without Clinical Manifestation of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
Objectives: Existing evidence suggests that impaired vitamin D metabolism contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. Aortic intima-media thickness (IMT) is an earlier marker than carotid IMT of preclinical atherosclerosis. However, there is a lack of researches on direct investigation of relevance between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and thoracic aortic IMT. In this study, we aimed to assess the relationship between thoracic aortic IMT and 25(OH)D.
Methods: We studied 117 patients (mean age: 45.5 ± 8.4 years) who underwent transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) for various indications. Serum 25(OH)D was measured using a direct competitive chemiluminescent immunoassay. The patients were divided into three groups according to the their serum 25(OH)D levels (VitDdeficiency , VitDinsufficient and VitDnormal groups). TEE was performed in all subjects. High sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and other biochemical markers were measured using an automated chemistry analyzer.
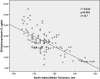
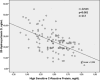
Results: Only 24.8% (29 patients) of patients had normal levels of 25(OH)D. The highest aortic IMT values were observed in VitDdeficiency group compared with VitDinsufficient and VitDnormal groups (P < 0.05, for all). Also aortic IMT values of VitDinsufficient group were higher than VitDnormal group (P < 0.05). 25(OH)D was independently associated with hs-CRP (β = -0.442, P < 0.001) and aortic IMT (β = -0.499, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The lower 25(OH)D level was independently associated with higher aortic IMT values. Therefore, hypovitaminosis D may have a role on pathogenesis of subclinical thoracic atherosclerosis.
Keywords: CRP; Vitamin D; echocardiography; intima-media.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aortic distensibility and aortic intima-media thickness in patients without clinical manifestation of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Echocardiography. 2013 Apr;30(4):407-13. doi: 10.1111/echo.12066. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Echocardiography. 2013. PMID: 23227955
-
Uric acid and high sensitive C-reactive protein are associated with subclinical thoracic aortic atherosclerosis.J Cardiol. 2013 Feb;61(2):144-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2012.08.023. Epub 2012 Nov 16. J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23159203
-
Gamma glutamyl transferase activity: relationship with thoracic aortic intima media thickness and inflammation.Herz. 2014 Sep;39(6):761-6. doi: 10.1007/s00059-013-3921-0. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Herz. 2014. PMID: 23934197
-
Epicardial fat thickness is associated with aortic intima-media thickness in patients without clinical manifestation of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Echocardiography. 2017 Aug;34(8):1146-1151. doi: 10.1111/echo.13600. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Echocardiography. 2017. PMID: 28670756
-
Mean platelet volume is associated with aortic intima-media thickness in patients without clinical manifestation of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Anatol J Cardiol. 2015 Sep;15(9):753-8. doi: 10.5152/akd.2014.5576. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Anatol J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25592097 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Vitamin D in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: An Updated Review of the Literature.Dis Markers. 2015;2015:580474. doi: 10.1155/2015/580474. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Dis Markers. 2015. PMID: 26576069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level Is Positively Associated with Vascular Reactivity Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Nutrients. 2024 May 23;16(11):1575. doi: 10.3390/nu16111575. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892508 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Peripheral Arterial Stiffness in Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3-5 Patients.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 11;14(12):2429. doi: 10.3390/nu14122429. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35745159 Free PMC article.
-
Continued Interest and Controversy: Vitamin D in HIV.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2018 Jun;15(3):199-211. doi: 10.1007/s11904-018-0401-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2018. PMID: 29713871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction and Validation of a Novel Butyrylation-Related Gene Signature Related to Prognosis, Clinical Implications, and Immune Microenvironment Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 18;10(4):3375-3388. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c06496. eCollection 2025 Feb 4. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39926543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scragg R, Sowers M, Bell C. Serum 25‐hydroxyvitamin D, diabetes, and ethnicity in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care 2004;27:2813–2818. - PubMed
-
- Lee P, Greenfield JR, Seibel MJ, Eisman JA, Center JR. Adequacy of vitamin D supplementation in severe deficiency is dependent on body mass index. Am J Med 2009;122:1056–1060. - PubMed
-
- Snijder MB, Lips P, Seidell JC, Visser M, et al. Vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone levels in relation to blood pressure: a population‐based study in older men and women. J Intern Med 2007;261:558–565. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous