Homelessness and risk of end-stage renal disease
- PMID: 25130236
- PMCID: PMC4285149
- DOI: 10.1353/hpu.2014.0136
Homelessness and risk of end-stage renal disease
Abstract
To identify homeless people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) who were at highest risk for end-stage renal disease (ESRD), we studied 982 homeless and 15,674 domiciled people with CKD receiving public health care. We developed four risk prediction models for the primary outcome of ESRD. Overall, 71 homeless and 888 domiciled people progressed to ESRD during follow-up (median: 6.6 years). Homeless people with CKD experienced significantly higher incidence rates of ESRD than poor but domiciled peers. Most homeless people who developed progressive CKD were readily identifiable well before ESRD using a prediction model with five common variables. We estimated that program following homeless people in the highest decile of ESRD risk would have captured 64-85% of those who eventually progressed to ESRD within five years. Thus, an approach targeting homeless people at high risk for ESRD appears feasible and could reduce substantial morbidity and costs incurred by this highly vulnerable group.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
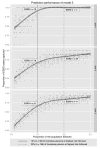
References
-
- Kushel MB, Vittinghoff E, Haas JS. Factors associated with the health care utilization of homeless people. JAMA. 2001 Jan 10;285(2):200–6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.285.2.200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hall YN, Choi AI, Himmelfarb J, et al. Homelessness and CKD: a cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jul;7(7):1094–102. http://dx.doi.org/10.2215/CJN.00060112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Larimer ME, Malone DK, Garner MD, et al. Health care and public service use and costs before and after provision of housing for chronically homeless people with severe alcohol problems. JAMA. 2009 Apr 1;301(13):1349–57. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.414. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sadowski LS, Kee RA, VanderWeele TJ, et al. Effect of a housing and case management program on emergency department visits and hospitalizations among chronically ill homeless adults: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2009 May 6;301(17):1771–8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.561. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hall YN, Choi AI, Chertow GM, et al. Chronic kidney disease in the urban poor. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 May;5(5):828–35. http://dx.doi.org/10.2215/CJN.09011209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
