ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development
- PMID: 25132496
- PMCID: PMC4165611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.001
ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development
Abstract
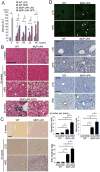
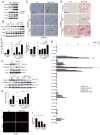
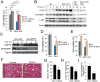
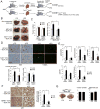
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been implicated in the pathogenesis of viral hepatitis, insulin resistance, hepatosteatosis, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), disorders that increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). To determine whether and how ER stress contributes to obesity-driven hepatic tumorigenesis we fed wild-type (WT) and MUP-uPA mice, in which hepatocyte ER stress is induced by plasminogen activator expression, with high-fat diet. Although both strains were equally insulin resistant, the MUP-uPA mice exhibited more liver damage, more immune infiltration, and increased lipogenesis and, as a result, displayed classical NASH signs and developed typical steatohepatitic HCC. Both NASH and HCC development were dependent on TNF produced by inflammatory macrophages that accumulate in the MUP-uPA liver in response to hepatocyte ER stress.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: at the crossroads of inflammation and metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma development.Cancer Cell. 2014 Sep 8;26(3):301-303. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.08.007. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 25203316
References
-
- Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: definition and pathology. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Teras LR, Thun MJ. Obesity and mortality. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2197–2199. - PubMed
-
- Chen CL, Yang HI, Yang WS, Liu CJ, Chen PJ, You SL, Wang LY, Sun CA, Lu SN, Chen DS, Chen CJ. Metabolic factors and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma by chronic hepatitis B/C infection: a follow-up study in Taiwan. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

