Disease mechanisms in rheumatology--tools and pathways: defining functional genetic variants in autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 25132667
- PMCID: PMC4298761
- DOI: 10.1002/art.38800
Disease mechanisms in rheumatology--tools and pathways: defining functional genetic variants in autoimmune diseases
Figures

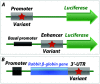
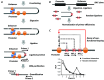
References
-
- Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, Blumenstiel B, et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science. 2002;296:2225–9. - PubMed
-
- Parkes M, Cortes A, van Heel DA, Brown MA. Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:661–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

