Multidisciplinary and evidence-based management of fistulizing perianal Crohn's disease
- PMID: 25133026
- PMCID: PMC4133523
- DOI: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.239
Multidisciplinary and evidence-based management of fistulizing perianal Crohn's disease
Abstract
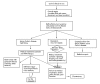
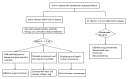
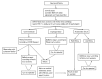
Perianal symptoms are common in patients with Crohn's disease and cause considerable morbidity. The etiology of these symptoms include skin tags, ulcers, fissures, abscesses, fistulas or stenoses. Fistula is the most common perianal manifestation. Multiple treatment options exist although very few are evidence-based. The phases of treatment include: drainage of infection, assessment of Crohn's disease status and fistula tracts, medical therapy, and selective operative management. The impact of biological therapy on perianal Crohn's disease is uncertain given that outcomes are conflicting. Operative treatment to eradicate the fistula tract can be attempted once infection has resolved and Crohn's disease activity is controlled. The operative approach should be tailored according to the anatomy of the fistula tract. Definitive treatment is challenging with medical and operative treatment rarely leading to true healing with frequent complications and recurrence. Treatment success must be weighed against the risk of complications, specially anal sphincter injury. A full understanding of the etiology and all potential therapeutic options is critical for success. Multidisciplinary management of fistulizing perianal Crohn's disease is crucial to improve outcomes.
Keywords: Abscess; Fistula; Management; Perianal Crohn’s disease; Review.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources