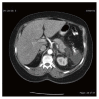
Statins and their role in acute pancreatitis: Case report and literature review
- PMID: 25133048
- PMCID: PMC4133445
- DOI: 10.4292/wjgpt.v5.i3.191
Statins and their role in acute pancreatitis: Case report and literature review
Abstract
Statin induced pancreatitis has historically been considered a diagnosis of exclusion, with literature references typically in the form of case reports and observational studies. Recently, larger studies have challenged the correlations made by earlier case reports, and instead demonstrate a mild protective effect in statin users. We present a case report of likely statin induced pancreatitis in a 58-year-old male (which we have attributed to drug-drug interaction with resulting inhibition of hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes) and have reviewed the apparent dichotomy in the available literature.
Keywords: CYP450; Inflammation; Pancreatitis; Statin; Toxic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pravastatin-Induced Acute Pancreatitis: A Case Report and Literature Review.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021 Jan-Dec;9:23247096211028386. doi: 10.1177/23247096211028386. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34180257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of statins and the risk of acute pancreatitis: a population-based case-control study.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2015 Oct;24(10):1085-92. doi: 10.1002/pds.3858. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2015. PMID: 26300102
-
Recurrent acute pancreatitis possibly induced by atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Is statin induced pancreatitis a class effect?JOP. 2004 Nov 10;5(6):502-4. JOP. 2004. PMID: 15536291
-
A case of simvastatin-associated pancreatitis and review of statin-associated pancreatitis.Pharmacotherapy. 2006 Mar;26(3):414-22. doi: 10.1592/phco.26.3.414. Pharmacotherapy. 2006. PMID: 16503723 Review.
-
Reduced risk of post ERCP pancreatitis in statin users.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Apr 23;20(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01264-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32326889 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pravastatin-Induced Acute Pancreatitis: A Case Report and Literature Review.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021 Jan-Dec;9:23247096211028386. doi: 10.1177/23247096211028386. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34180257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statins exposure and acute pancreatitis: a retrospective cohort study using a large national insurance database.BMJ Open. 2023 Sep 27;13(9):e077591. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077591. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37758671 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease with large-size vessel involvement is more diverse than originally thought.J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2022 Jul 31;8(4):872. doi: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2022.07.005. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2022. PMID: 36568955 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Statin Therapy and Pancreatitis: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Jan 5;16(1):e51723. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51723. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38318563 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-core nanocapsules containing simvastatin do not affect the biochemical and hematological indicators of toxicity in rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Nov 12;13(6):tfae189. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae189. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39539252
References
-
- Eland IA, van Puijenbroek EP, Sturkenboom MJ, Wilson JH, Stricker BH. Drug-associated acute pancreatitis: twenty-one years of spontaneous reporting in The Netherlands. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:2417–2422. - PubMed
-
- Vinklerová I, Procházka M, Procházka V, Urbánek K. Incidence, severity, and etiology of drug-induced acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:2977–2981. - PubMed
-
- Grendell JH. Editorial: drug-induced acute pancreatitis: uncommon or commonplace? Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:2189–2191. - PubMed
-
- Badalov N, Baradarian R, Iswara K, Li J, Steinberg W, Tenner S. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis: an evidence-based review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:648–661; quiz 644. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources