Comments on the mechanisms of action of radiation protective agents: basis components and their polyvalence
- PMID: 25133093
- PMCID: PMC4132458
- DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-414
Comments on the mechanisms of action of radiation protective agents: basis components and their polyvalence
Abstract
Purpose: These comments suggest a division of radiation protective agents on the grounds of their mechanism of action that increase the radio resistance of an organism.
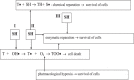
Conclusion: Given below is the division of radiation protective agents on the basis of their mechanism of action into 3 groups: 1) Radiation protective agents, with the implementation of radiation protective action taking place at the cellular level in the course of rapidly proceeding radiation-chemical reactions. At the same time, when the ionizing radiation energy is absorbed, these agents partially neutralize the "oxygen effect" as a radiobiological phenomenon, especially in the radiolysis of DNA; 2) Radiation protective agents that exert their effect at the system level by accelerating the post-radiation recovery of radiosensitive tissues through activation of a number of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways and an increase in the secretion of hematopoietic growth factors, including their use as mitigators in the early period after irradiation prior to the clinical development of acute radiation syndrome (ARS). 3) Radiomodulators including drugs and nutritional supplements that can elevate the resistance of the organism to adverse environmental factors, including exposure to ionization by means of modulating the gene expression through a hormetic effect of small doses of stressors and a "substrate" maintenance of adaptive changes, resulting in an increased antioxidant protection of the organism. Radiation protective agents having polyvalence in implementation of their action may simultaneously induce radioprotective effect by various routes with a prevalence of basis mechanisms of the action.
Keywords: Mechanism of action; Radiomitigator; Radiomodulator; Radioprotector.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The classification of radiation protective agents as the reflection of the present state and development perspective, of current radiation pharmacology].Radiats Biol Radioecol. 2013 Sep-Oct;53(5):459-67. Radiats Biol Radioecol. 2013. PMID: 25434165 Russian.
-
Radiation protection following nuclear power accidents: a survey of putative mechanisms involved in the radioprotective actions of taurine during and after radiation exposure.Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2012 Feb 1;23. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v23i0.14787. eCollection 2012. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 23990836 Free PMC article.
-
ASSESSMENT OF RADIOPROTECTIVE ACTION OF BASIDIOMYCOTIC MELANIN PIGMENTS ON THE HEMATOPOIETIC SYSTEM OF Balb/C MICE UNDER EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION IN SUBLETHAL DOSE.Probl Radiac Med Radiobiol. 2019 Dec;24:210-219. doi: 10.33145/2304-8336-2019-24-210-219. Probl Radiac Med Radiobiol. 2019. PMID: 31841468 English, Ukrainian.
-
Concerted action of Nrf2-ARE pathway, MRN complex, HMGB1 and inflammatory cytokines - implication in modification of radiation damage.Redox Biol. 2014 Feb 28;2:832-46. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.02.008. eCollection 2014. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 25009785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiosensitizers, radioprotectors, and radiation mitigators.Indian J Dent Res. 2014 Jan-Feb;25(1):83-90. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.131142. Indian J Dent Res. 2014. PMID: 24748306 Review.
Cited by
-
MDP: A Deinococcus Mn2+-Decapeptide Complex Protects Mice from Ionizing Radiation.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 8;11(8):e0160575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160575. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27500529 Free PMC article.
-
Radioprotective Role of Peroxiredoxin 6.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Jan 5;8(1):15. doi: 10.3390/antiox8010015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30621289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immuno-protective impact and clinical translation of radioprotective agents in cancer radiotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 4;16:1610296. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1610296. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40688089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Profiling Reveals a Common Mechanism of Histone Gene Downregulation and Complementary Effects for Radioprotectants in Response to Ionizing Radiation.Dose Response. 2020 Oct 16;18(4):1559325820968433. doi: 10.1177/1559325820968433. eCollection 2020 Oct-Dec. Dose Response. 2020. PMID: 33117095 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of the stressed supernatant from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis and its metabolic analysis.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Jun 25;204(7):428. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-03034-1. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35751720
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Takada Y, Shishodia S, Gutierrez AM, Oommen OV, Ichikawa H, Baba Y, Kumar A. Nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B: role in biology and medicine. Indian J Exp Biol. 2004;42:341–353. - PubMed
-
- Alexander P, Charlesby A. Physico-chemical methods of protection against ionizing radiations. Butterworth, London: Radiobiological Symposium Liege; 1954. pp. 49–59.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

