Open fenestration for complicated acute aortic B dissection
- PMID: 25133107
- PMCID: PMC4128920
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2225-319X.2014.07.08
Open fenestration for complicated acute aortic B dissection
Abstract
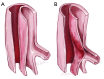
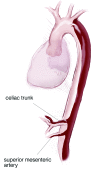
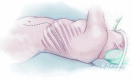
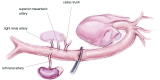
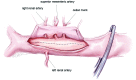
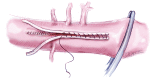
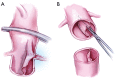
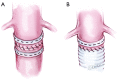
Acute type B aortic dissection (ABAD) is a serious cardiovascular emergency in which morbidity and mortality are often related to the presence of complications at clinical presentation. Visceral, renal, and limb ischemia occur in up to 30% of patients with ABAD and are associated with higher in-hospital mortality. The aim of the open fenestration is to resolve the malperfusion by creating a single aortic lumen at the suprarenal or infrarenal level. This surgical procedure is less invasive than total aortic replacement, thus not requiring extracorporeal support and allowing preservation of the intercostal arteries, which results in decreased risk of paraplegia. Surgical aortic fenestration represents an effective and durable option for treating ischemic complications of ABAD, particularly for patients with no aortic dilatation. In the current endovascular era, this open technique serves as an alternative option in case of contraindications or failure of endovascular management of complicated ABAD.
Keywords: Acute type B aortic dissection; malperfusion; open fenestration.
Figures




References
-
- Gurin D, Bulmer JW, Derby R. Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: diagnosis and operative relief of acute arterial obstruction due to this cause. NY State J Med 1935;35:1200-2
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
