Evaluation and management of caustic injuries from ingestion of Acid or alkaline substances
- PMID: 25133115
- PMCID: PMC4130883
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.4.301
Evaluation and management of caustic injuries from ingestion of Acid or alkaline substances
Abstract
Although the numbers have decreased compared with in the past, cases of patients who ingest caustic substances and visit the emergency room are not rare. However, well-summarized data about caustic injuries are insufficient. Therefore, in this article, I will discuss the etiologic causative agents, injury mechanism, and clinical characteristics, as well as the endoscopic evaluation of the degree of injury and proper management of the patient, in gastrointestinal caustic injury.
Keywords: Acids; Alkalies; Caustic injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
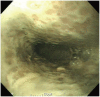


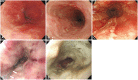
References
-
- Goldman LP, Weigert JM. Corrosive substance ingestion: a review. Am J Gastroenterol. 1984;79:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Riffat F, Cheng A. Pediatric caustic ingestion: 50 consecutive cases and a review of the literature. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Gumaste VV, Dave PB. Ingestion of corrosive substances by adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Yeom HJ, Shim KN, Kim SE, et al. Clinical characteristics and predisposing factors for complication of caustic injury of the upper digestive tract. Korean J Med. 2006;70:371–377.
-
- Yoon KW, Park MH, Park GS, et al. A clinical study on the upper gastrointestinal tract injury caused by corrosive agent. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;23:82–87.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

