SIN3 is critical for stress resistance and modulates adult lifespan
- PMID: 25133314
- PMCID: PMC4169859
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100684
SIN3 is critical for stress resistance and modulates adult lifespan
Abstract
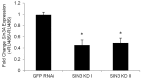
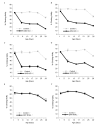
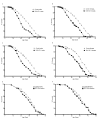
Coordinate control of gene activity is critical for fitness and longevity of an organism. The SIN3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex functions as a transcriptional repressor of many genes. SIN3-regulated genes include those that encode proteins affecting multiple aspects of mitochondrial function, such as energy production and stress responsiveness, important for health maintenance. Here we used Drosophila melanogaster as a model organism to examine the role of SIN3 in the regulation of fitness and longevity. Adult flies with RNA interference (RNAi) induced knockdown expression of Sin3A have reduced climbing ability; an activity that likely requires fully functional mitochondria. Additionally, compared to wild type, adult Sin3A knockdown flies were more sensitive to oxidative stress. Interestingly, media supplementation with the antioxidant glutathione largely restored fly tolerance to oxidative stress. Although Sin3A knockdown flies exhibited decreased longevity compared to wild type, no significant changes in expression of many well-categorized aging genes were observed. We found, however, that Sin3A knockdown corresponded to a significant reduction in expression of genes encoding proteins involved in the de novo synthesis of glutathione. Taken together, the data support a model whereby SIN3 regulates a gene expression program required for proper mitochondrial function and effective stress response during adulthood.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ROS is the major player in regulating altered autophagy and lifespan in sin-3 mutants of C. elegans.Autophagy. 2018;14(7):1239-1255. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1474312. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29912629 Free PMC article.
-
A complex interplay between SAM synthetase and the epigenetic regulator SIN3 controls metabolism and transcription.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 10;295(2):375-389. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010032. Epub 2019 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31776190 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the SIN3 transcriptional corepressor results in aberrant mitochondrial function.BMC Biochem. 2010 Jul 9;11:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-11-26. BMC Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20618965 Free PMC article.
-
Sin3: insight into its transcription regulatory functions.Eur J Cell Biol. 2013 Aug-Sep;92(8-9):237-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24189169 Review.
-
Co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor: the many faces of the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex.Biochem J. 2018 Dec 14;475(24):3921-3932. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170314. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30552170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ROS is the major player in regulating altered autophagy and lifespan in sin-3 mutants of C. elegans.Autophagy. 2018;14(7):1239-1255. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1474312. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29912629 Free PMC article.
-
SIN-3 as a key determinant of lifespan and its sex dependent differential role on healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans.Aging (Albany NY). 2018 Dec 12;10(12):3910-3937. doi: 10.18632/aging.101682. Aging (Albany NY). 2018. PMID: 30541942 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin: the old and young of it.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Oct 9;10:1270285. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1270285. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37877123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila O-GlcNAcase Mutants Reveal an Expanded Glycoproteome and Novel Growth and Longevity Phenotypes.Cells. 2021 Apr 27;10(5):1026. doi: 10.3390/cells10051026. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33925313 Free PMC article.
-
The Transcriptional Corepressor SIN3 Directly Regulates Genes Involved in Methionine Catabolism and Affects Histone Methylation, Linking Epigenetics and Metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 3;292(5):1970-1976. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.749754. Epub 2016 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28028175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zentner GE, Henikoff S. Regulation of nucleosome dynamics by histone modifications. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Nagy Z, Tora L. Distinct GCN5/PCAF-containing complexes function as co-activators and are involved in transcription factor and global histone acetylation. Oncogene. 2007;26:5341–5357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

