Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) in murine brachiocephalic and carotid atherosclerotic lesions
- PMID: 25133350
- PMCID: PMC4181795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.07.029
Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) in murine brachiocephalic and carotid atherosclerotic lesions
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the hypothesis that COMP can influence the morphology, stability and size of murine atherosclerotic lesions.
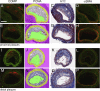
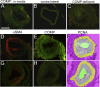
Methods: ApoE- and ApoE/COMP-knockout mice were fed a high-fat diet to develop atherosclerotic plaques at lesion sites of three different types; inflammatory and fibrous plaques induced in the carotid artery by low or oscillatory shear stress, respectively, and spontaneously developing plaques in the brachiocephalic artery. The localization of COMP in the plaques and the effect of COMP deficiency on plaque development were evaluated.
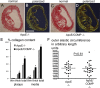
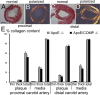
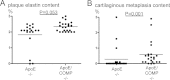
Results: COMP immunoreactivity was observed in about half of the investigated plaques from the ApoE null mice, mainly located along the intima-medial border. There were no significant differences in the size of inflammatory and fibrous carotid plaques between the genotypes. Plaques in the brachiocephalic artery from ApoE mice lacking COMP were increased in size with 54%. In these plaques the collagen content was also increased by 48%. There were no differences in relative collagen content in inflammatory and fibrous carotid plaques between genotypes. Polarized light microscopy showed that the increase in total collagen in brachiocephalic plaques was more than proportionally accounted for by an increase in thicker collagen fibrils.
Conclusion: We have shown that COMP deficiency has a significant impact on atherosclerotic plaque morphology and size. Our data also suggest that an altered collagen metabolism may be an important mechanism in this finding.
Keywords: ApoE-KO mouse; Atherosclerosis; COMP; Collagen fibre; Plaque morphology.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein Associates With a Vulnerable Plaque Phenotype in Human Atherosclerotic Plaques.Stroke. 2019 Nov;50(11):3289-3292. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026457. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Stroke. 2019. PMID: 31495329
-
Fibromodulin deficiency reduces low-density lipoprotein accumulation in atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-null mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Feb;33(2):354-61. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300723. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23202368
-
Shift of Macrophage Phenotype Due to Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein Deficiency Drives Atherosclerotic Calcification.Circ Res. 2016 Jul 8;119(2):261-76. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.308021. Epub 2016 May 5. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27151399
-
The fat-fed apolipoprotein E knockout mouse brachiocephalic artery in the study of atherosclerotic plaque rupture.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:379069. doi: 10.1155/2011/379069. Epub 2010 Nov 7. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21076539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial omics strategies for investigating human carotid atherosclerotic disease.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Apr;15(4):e70277. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70277. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40156163 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of ADAMTS‑7 and downregulation of COMP are associated with spontaneous abortion.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Apr;19(4):2620-2626. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9898. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30720083 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Cause or Consequence of Vascular Calcification?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 16;9:611922. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.611922. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33816463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel therapeutic interventions for pseudoachondroplasia.Bone. 2017 Sep;102:60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.03.045. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Bone. 2017. PMID: 28336490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Extracellular Matrix in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 8;25(22):12017. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212017. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular disease risk in early rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and disease activity.BMC Rheumatol. 2023 Dec 1;7(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s41927-023-00367-2. BMC Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 38037148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson C.L., Bennett M.R., Biessen E.A., Johnson J.L., Krams R. Assessment of unstable atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:714–720. - PubMed
-
- Halasz K., Kassner A., Morgelin M., Heinegard D. COMP acts as a catalyst in collagen fibrillogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:31166–31173. - PubMed
-
- Riessen R., Fenchel M., Chen H., Axel D.I., Karsch K.R. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (thrombospondin-5) is expressed by human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Strom A., Ahlqvist E., Franzen A., Heinegard D., Hultgardh-Nilsson A. Extracellular matrix components in atherosclerotic arteries of Apo E/LDL receptor deficient mice: an immunohistochemical study. Histol Histopathol. 2004;19:337–347. - PubMed
-
- Dickinson S.C., Vankemmelbeke M.N., Buttle D.J., Rosenberg K., Heinegard D. Cleavage of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (thrombospondin-5) by matrix metalloproteinases and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs. Matrix Biol. 2003;22:267–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

