Esophageal diseases
- PMID: 25133481
- PMCID: PMC4772736
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1377508
Esophageal diseases
Figures
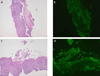
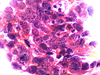
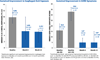

References
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA, et al. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 May;108(5):679–692. quiz 693. - PubMed
-
- Katzka DA, Ravi A, Geno DM, Smyrk TC, Kita H, Lao-Sirieix P, et al. Cytosponge Evaluation of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Comparison to Endoscopy: Accuracy, Safety and Tolerability. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(5):S16. - PubMed
-
- American Gastroenterological Association. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(3):1084–1091. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

