Is thymidine glycol containing DNA a substrate of E. coli DNA mismatch repair system?
- PMID: 25133614
- PMCID: PMC4136841
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104963
Is thymidine glycol containing DNA a substrate of E. coli DNA mismatch repair system?
Erratum in
-
Correction: Is Thymidine Glycol Containing DNA a Substrate of E. coli DNA Mismatch Repair System?PLoS One. 2015 Feb 10;10(2):e0118035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118035. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25668755 Free PMC article.
Abstract
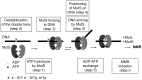
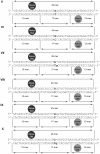
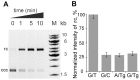
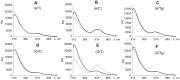
The DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system plays a crucial role in the prevention of replication errors and in the correction of some oxidative damages of DNA bases. In the present work the most abundant oxidized pyrimidine lesion, 5,6-dihydro-5,6-dihydroxythymidine (thymidine glycol, Tg) was tested for being recognized and processed by the E. coli MMR system, namely complex of MutS, MutL and MutH proteins. In a partially reconstituted MMR system with MutS-MutL-MutH proteins, G/Tg and A/Tg containing plasmids failed to provoke the incision of DNA. Tg residue in the 30-mer DNA duplex destabilized double helix due to stacking disruption with neighboring bases. However, such local structural changes are not important for E. coli MMR system to recognize this lesion. A lack of repair of Tg containing DNA could be due to a failure of MutS (a first acting protein of MMR system) to interact with modified DNA in a proper way. It was shown that Tg in DNA does not affect on ATPase activity of MutS. On the other hand, MutS binding affinities to DNA containing Tg in G/Tg and A/Tg pairs are lower than to DNA with a G/T mismatch and similar to canonical DNA. Peculiarities of MutS interaction with DNA was monitored by Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence anisotropy. Binding of MutS to Tg containing DNAs did not result in the formation of characteristic DNA kink. Nevertheless, MutS homodimer orientation on Tg-DNA is similar to that in the case of G/T-DNA. In contrast to G/T-DNA, neither G/Tg- nor A/Tg-DNA was able to stimulate ADP release from MutS better than canonical DNA. Thus, Tg residue in DNA is unlikely to be recognized or processed by the E. coli MMR system. Probably, the MutS transformation to active "sliding clamp" conformation on Tg-DNA is problematic.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Dolinnaya NG, Kubareva EA, Romanova EA, Trikin RM, Oretskaya TS (2013) Thymidine glycol: the effect on DNA molecular structure and enzymatic processing. Biochimie 95: 134–147. - PubMed
-
- McTigue MM, Rieger RA, Rosenquist TA, Iden CR, De Los Santos CR (2004) Stereoselective excision of thymine glycol lesions by mammalian cell extracts. DNA Repair (Amst) 3: 313–322. - PubMed
-
- Brown KL, Roginskaya M, Zou Y, Altamirano A, Basu AK, et al. (2010) Binding of the human nucleotide excision repair proteins XPA and XPC/HR23B to the 5R-thymine glycol lesion and structure of the cis-(5R,6S) thymine glycol epimer in the 5′-GTgG-3′ sequence: destabilization of two base pairs at the lesion site. Nucleic Acids Res 38: 428–440. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

