Protein supplementation increases postexercise plasma myostatin concentration after 8 weeks of resistance training in young physically active subjects
- PMID: 25133710
- PMCID: PMC4281872
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2014.0004
Protein supplementation increases postexercise plasma myostatin concentration after 8 weeks of resistance training in young physically active subjects
Abstract
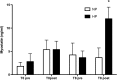
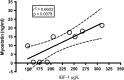
Myostatin (MSTN) is a negative regulator of muscle growth even if some studies have shown a counterintuitive positive correlation between MSTN and muscle mass (MM). Our aim was to investigate the influence of 2 months of resistance training (RT) and diets with different protein contents on plasma MSTN, interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). Eighteen healthy volunteers were randomly divided in two groups: high protein (HP) and normal protein (NP) groups. Different protein diet contents were 1.8 and 0.85 g of protein·kg bw(-1)·day(-1) for HP and NP, respectively. Subjects underwent 8 weeks of standardized progressive RT. MSTN, IGF-1, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were analyzed before and after the first and the last training sessions. Lean body mass, MM, upper-limb muscle area, and strength were measured. Plasma MSTN showed a significant increase (P<.001) after the last training in the HP group compared with NP group and with starting value. IGF-1 plasma concentration showed a positive correlation with MSTN in HP after the last training (r(2)=0.6456; P=.0295). No significant differences were found between NP and HP for IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and strength and MM or area. These findings suggest a "paradoxical" postexercise increase of plasma MSTN after 8 weeks of RT and HP diets. This MSTN elevation correlates positively with IGF-1 plasma level. This double increase of opposite (catabolic/anabolic) mediators could explain the substantial overlapping of MM increases in the two groups.
Keywords: cytokines; diet; exercise; myostatin; nutritional supplement.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myostatin alters with exercise training in diabetic rats; possible interaction with glycosylated hemoglobin and inflammatory cytokines.Cytokine. 2019 Aug;120:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 May 1. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 31054482
-
The correlation of resistance exercise-induced myostatin with insulin resistance and plasma cytokines in healthy young men.J Endocrinol Invest. 2016 Apr;39(4):383-8. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0373-9. Epub 2015 Aug 18. J Endocrinol Invest. 2016. PMID: 26280319 Clinical Trial.
-
Supplementing With Which Form of Creatine (Hydrochloride or Monohydrate) Alongside Resistance Training Can Have More Impacts on Anabolic/Catabolic Hormones, Strength and Body Composition?Physiol Res. 2024 Nov 15;73(5):739-753. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935323. Physiol Res. 2024. PMID: 39545789 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Myostatin and muscle atrophy during chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021 Nov 9;36(11):1986-1993. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa129. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021. PMID: 32974666 Review.
-
Myokines and Resistance Training: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 23;23(7):3501. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073501. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of serum myokines and aerobic exercise training in patients with spinal cord injury: an observational study.BMC Neurol. 2016 Aug 17;16(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0661-9. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27534935 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Resting Metabolic Rate in Adults with Hemiparetic Chronic Stroke.J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2015 Dec 22;6(6):1000341. doi: 10.4172/2155-9562.1000341. J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26973796 Free PMC article.
-
Anabolic myokine responses and muscular performance following 8 weeks of autoregulated compared to linear resistance exercise in recreationally active males.Hormones (Athens). 2024 Sep;23(3):487-496. doi: 10.1007/s42000-024-00544-z. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Hormones (Athens). 2024. PMID: 38472648 Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of the effect of protein supplementation on resistance training-induced gains in muscle mass and strength in healthy adults.Br J Sports Med. 2018 Mar;52(6):376-384. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-097608. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Br J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 28698222 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-enriched soup and weekly exercise improve muscle health: A randomized trial in mid-to-old age with inadequate protein intake.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024 Aug;15(4):1348-1357. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13481. Epub 2024 Apr 20. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024. PMID: 38641937 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wilborn CD, Taylor LW, Greenwood M, Kreider RB, Willoughby DS: Effects of different intensities of resistance exercise on regulators of myogenesis. J Strength Cond Res 2009;23:2179–2187 - PubMed
-
- Dodd KM, Tee AR: Leucine and mTORC1: a complex relationship. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2012;302:E1329–E1342 - PubMed
-
- Elliott B, Renshaw D, Getting S, Mackenzie R: The central role of myostatin in skeletal muscle and whole body homeostasis. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2012;205:324–340 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

