A Review of the Evidence for Using Bedaquiline (TMC207) to Treat Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis
- PMID: 25134476
- PMCID: PMC4108107
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-013-0009-3
A Review of the Evidence for Using Bedaquiline (TMC207) to Treat Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis
Abstract
Existing therapies for multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) have substantial limitations, in terms of their effectiveness, side-effect profile, and complexity of administration. Bedaquiline is a novel diarylquinoline antibiotic that has recently been investigated as an adjunct to existing therapies for MDR-TB. Currently, limited clinical data are available to evaluate the drug's safety and effectiveness. In two small randomized-controlled clinical studies, bedaquiline given for 8 or 24 weeks has been shown to improve surrogate microbiological markers of treatment response, but trials have not yet evaluated its impact on clinical failure and relapse. Safety concerns include an increased mortality in the bedaquiline arm of one study, an increased incidence of QT segment prolongation on electrocardiogram, and hepatotoxicity. Until further research data are available, the use of bedaquiline should be confined to settings where carefully selected patients can be closely monitored.
Figures
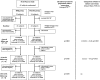
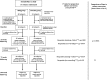
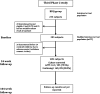
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis control 2012. Geneva: 2012. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed on 1 May 2013.
-
- World Health Organization. Treatment of tuberculosis guidelines. Geneva: 2010. http://www.who.int/tb/features_archive/new_treatment_guidelines_may2010/.... Accessed on 1 May 2013.
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Geneva 2011. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241501583_eng.pdf. Accessed on 1 May 2013. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

