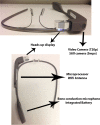
The virtual toxicology service: wearable head-mounted devices for medical toxicology
- PMID: 25135308
- PMCID: PMC4252294
- DOI: 10.1007/s13181-014-0420-5
The virtual toxicology service: wearable head-mounted devices for medical toxicology
Figures
References
-
- Field MJ. Institute of medicine committee on evaluating clinical applications of telemedicine: a guide to assessing telecommunications in health care, National Academies Press (US) Washington (DC): National Academy of Sciences; 1996. - PubMed
-
- Starr P. The social transformation of American medicine. Basic: Books; 1984.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources