p38 MAPK in pancreatic cancer: finding a protective needle in the haystack
- PMID: 25135483
- PMCID: PMC4254114
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1543
p38 MAPK in pancreatic cancer: finding a protective needle in the haystack
Abstract
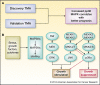
Activated p38 MAPK alpha (pp38α) is a good prognostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma that could be used to personalize therapy. pp38α suppresses JNK-mediated proliferation, both in vitro and in vivo. These findings support the testing of combination therapies that include JNK targeting and/or suppressing negative regulators of pp38α.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Comment on
-
Functional p38 MAPK identified by biomarker profiling of pancreatic cancer restrains growth through JNK inhibition and correlates with improved survival.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 1;20(23):6200-11. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2823. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24963048 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

