Vascular endothelial growth factor in anterior chamber liquid patients with diabetic retinopathy, cataract and neovascular glaucoma
- PMID: 25135700
- PMCID: PMC4108152
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-013-0014-3
Vascular endothelial growth factor in anterior chamber liquid patients with diabetic retinopathy, cataract and neovascular glaucoma
Abstract
Introduction: The aims of this study were: (1) to investigate the association of vascular endothelial growth factor isoform A (VEGF-A) concentration in the anterior chamber liquid (ACL) with vascular proliferation in patients with diabetic retinopathy (DR) who had undergone surgical treatment for cataract and neovascular glaucoma; (2) to analyze the association of VEGF-A level in ACL with the cataract surgery outcomes.
Materials and methods: Undiluted aqueous fluid samples were obtained from 207 eyes of patients who underwent intraocular surgery, 136 patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) and 22 patients without DM. The ACL samples were obtained during operation. The VEGF-A levels were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
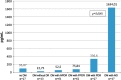
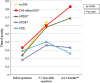
Results: The lowest VEGF-A levels were in diabetic patients without signs of DR [22.75 pg/mL (10.78; 63.36)]. More severe DR tended to occur in diabetic patients with higher VEGF-A levels in ACL. In diabetic patients with proliferative DR (PDR), VEGF-A levels were significantly higher [336.6 pg/mL (232.3; 410.74)] than in patients without DR P < 0.0001. In patients with terminal stage of DR [neovascular glaucoma (NG)], VEGF-A levels were dramatically higher and attained 1,634.01 pg/mL (610.69; 2657.33). In non-diabetic patients, VEGF-A levels were 95.07 pg/ml (60.92; 129.22). The best visual acuity results in post-operative period were observed in the group of diabetic patients without DR. In the group of patients with PDR, post-operative visual acuity [0.26 (0.1; 0.42)] was similar to visual acuity before operation [0.29 (0.13; 0.44)]. There was no significant increase in visual acuity due to cataract surgery. In 52.4% patients, no complications had occurred by the end of the follow-up period. In 40% patients, retinal laser coagulation was performed, and in 7.6% patients NG had developed.
Conclusion: VEGF-A level in ACL increases with DR progression and may be of prognostic value in evaluating the potential risk of further neovascularization progression in diabetic patients.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Sight test and glasses could dramatically improve the lives of 150 million people with poor vision. Press release, 11 October 2006. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2006/pr55/en/index.html (Accessed 1 Dec 2012). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

